Figure 6.
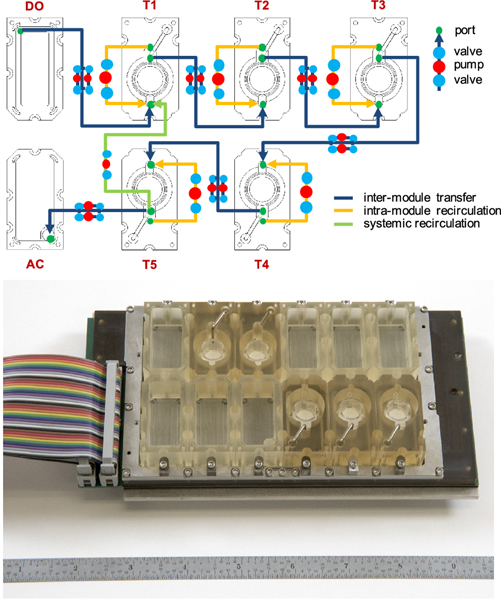
The microfluidic platform of ‘EVATAR’ that can interconnect different tissues/organs to make a female reproductive system-on-a-chip [53]. The system was designed based on pneumatic actuation technology. The interconnection between different modules was accomplished by embedding electromagnetically actuated micro-pumps and microfluidic channels. Each module allowed for recirculation within each module (orange), ensuring that the system was well mixed and enabling homogenous exposure of cultured tissues to factors within the media. Additionally, the fluidic path design also allowed for whole-system recirculation (blue), which enabled a well-mixed system within and across all tissue/organ modules. DO: donor module, T: tissue module, AC: acceptor module.