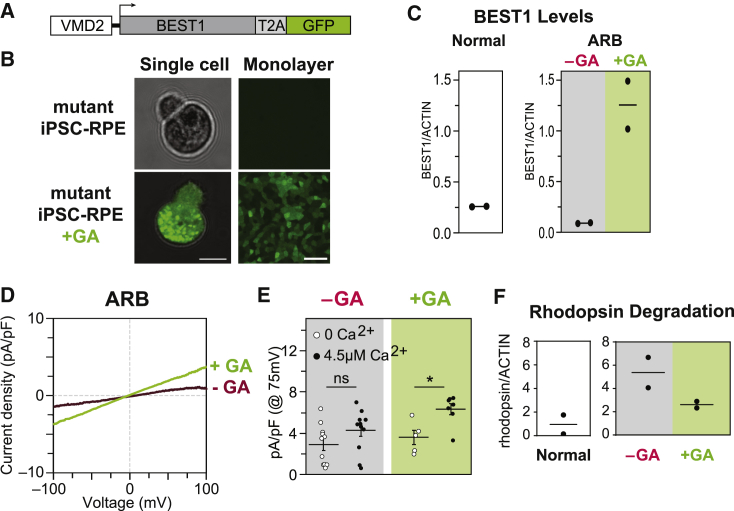
Figure 2.
Gene Augmentation Rescues the ARB iPSC-RPE Cell Phenotype
(A) Construct used for BEST1 augmentation (GA).
(B) Presence or absence of GFP fluorescence in a single dissociated iPSC-RPE cell (left) or iPSC-RPE monolayers (right) before (top) or after (bottom) gene augmentation. Scale bar = 10 μm (left); 50 μm (right).
(C) Immunoblot-based quantification of BEST1 levels (normalized to ACTIN) in WT iPSC-RPE (left), and in ARB iPSC-RPE before or after BEST1 augmentation (right).
(D) CaCC current density-voltage plots before and after gene augmentation in ARB iPSC-RPE. The -GA trace is the same as shown in Figure 1E. For the +GA trace, n = 7 cells for +calcium and 5 cells for no calcium (data combined from two replicates [Figure S2]).
(E) CaCC conductance for individual ARB iPSC-RPE cells at 75 mV before or after gene augmentation. The number of cells is the same as for panels 1E and 2D. Error bars represent mean ± SEM; ns = p ≥ 0.05, ∗ for p < 0.05. Black circles, +calcium condition; white circles, no calcium condition.
(F) Immunoblot-based quantification of rhodopsin levels 120 h after photoreceptor outer segment (POS) feeding in WT iPSC-RPE or in ARB iPSC-RPE before or after WT BEST1 augmentation.