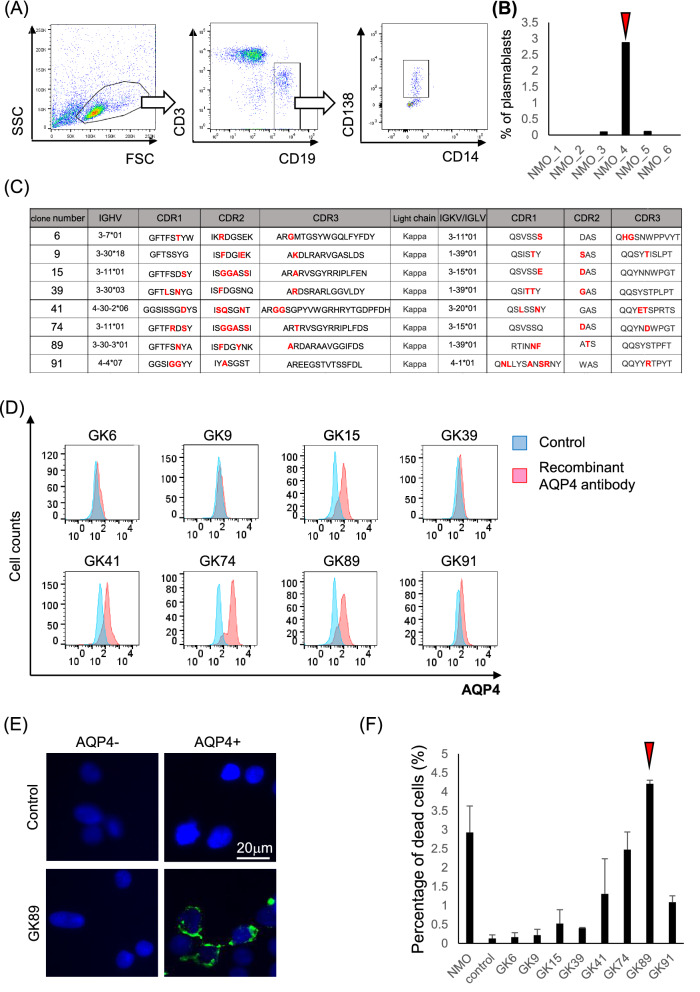
Figure 1.
Generation of pathogenic anti-AQP4 recombinant antibodies derived from patients’ plasmablasts. (A) CD3- CD19int CD138+ plasmablasts are isolated from patients’ CSF lymphocytes. (B) The highest percentage of plasmablasts is observed in the sample derived from patient 4 (arrow head). (C) The interclonal diversity of V regions of eight clones which showed positive binding to AQP4 are shown in red. (D) Immunoreactivity to AQP4-expressing HEK293 cells is assessed by FACS analysis. The clones GK15, 41, 74 and 89 show remarkable binding to AQP4. (E) The immunoreactivity of clones GK89 to AQP4-expressing HEK293 cells is shown. (F) The percentage of damaged cells is measured by LDH assay. Clone GK89 has the highest capacity to induce complement-dependent cytotoxicity (arrow head). Error bars indicate SEM.