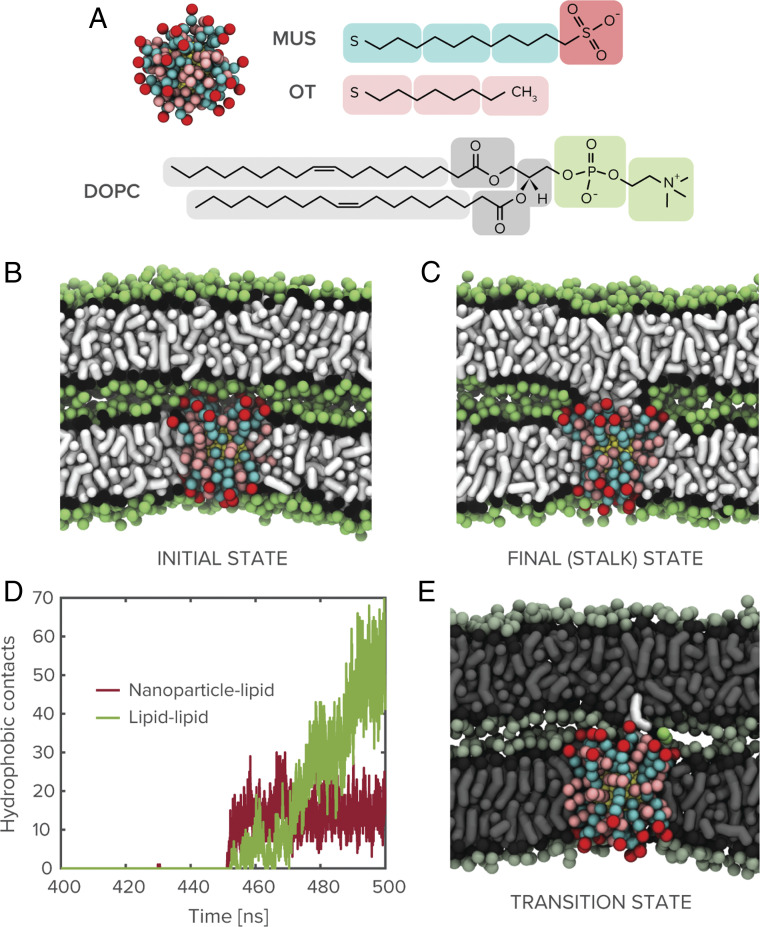
Fig. 1.
System components and nanoparticle-mediated stalk formation. (A) Coarse-grained representation of the amphiphilic MUS:OT nanoparticles studied in molecular dynamics simulations shown alongside chemical structure of the nanoparticle surface ligands and a DOPC lipid molecule. (B and C) Snapshots of initial simulation state and nanoparticle-induced stalk between dehydrated lipid membranes (water molecules not shown for clarity). (D) Time series plot of hydrophobic (alkyl-alkyl) contacts between nanoparticle and lipids from apposed bilayer and between lipids from the two bilayers. (E) Transition state for nanoparticle-mediated stalk formation, identified through committor analysis of the 2-nm MUS:OT trajectory, involves the extraction of a lipid from the adjacent bilayer toward the membrane-embedded nanoparticle.