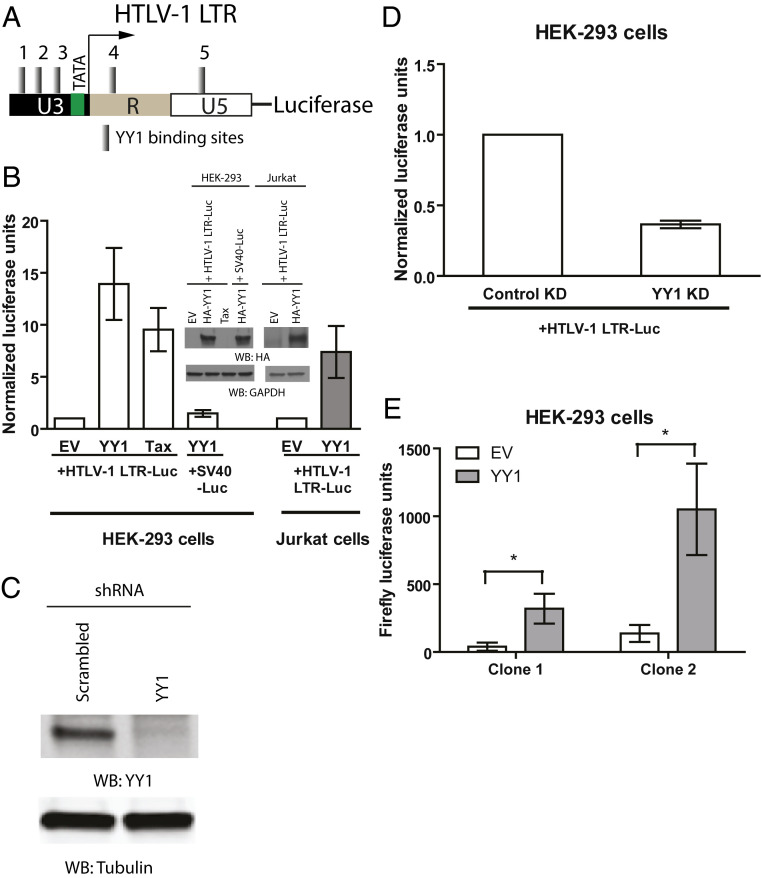
Fig. 1.
YY1 transactivates reporter expression from HTLV-1 LTR. (A) Schematic of predicted YY1 DNA-binding sites in HTLV-1 LTR. YY1-binding sites are numbered as indicated. (B) HEK-293 or Jurkat cells were transfected with empty vector (EV) or DNAs encoding YY1 or Tax, together with HTLV-1 LTR firefly luciferase or SV40 early promoter firefly luciferase, and HSV-TK Renilla luciferase control plasmid. Relative luciferase expression was calculated by first dividing the firefly luciferase signal by the Renilla luciferase signal in a given cell line, and the resulting ratio was then normalized to the ratio obtained from EV-transfected cells (set to 1). Results shown are means ± SEs from three independent experiments performed in duplicate. HA-YY1 overexpression is confirmed with Western blotting (WB) using an anti-HA antibody (Upper). (C) Lysate prepared from HEK-293 cells stably transduced with either control shRNA or YY1-specific shRNA were subjected to WB as indicated. (D) Similar assay in B in YY1 knockdown cells. Results shown are means ± SEs from three independent experiments performed in duplicate. (E) Cells with stably integrated HTLV-1 LTR luciferase reporter were transfected with EV or plasmid expressing YY1. Forty-eight hours later the activity of HTLV-1 LTR was determined by firefly luciferase assay. Data shown are mean firefly luciferase signal ± SEs from four independent experiments performed in duplicate. Student’s t test was used for statistical analysis. *P < 0.05.