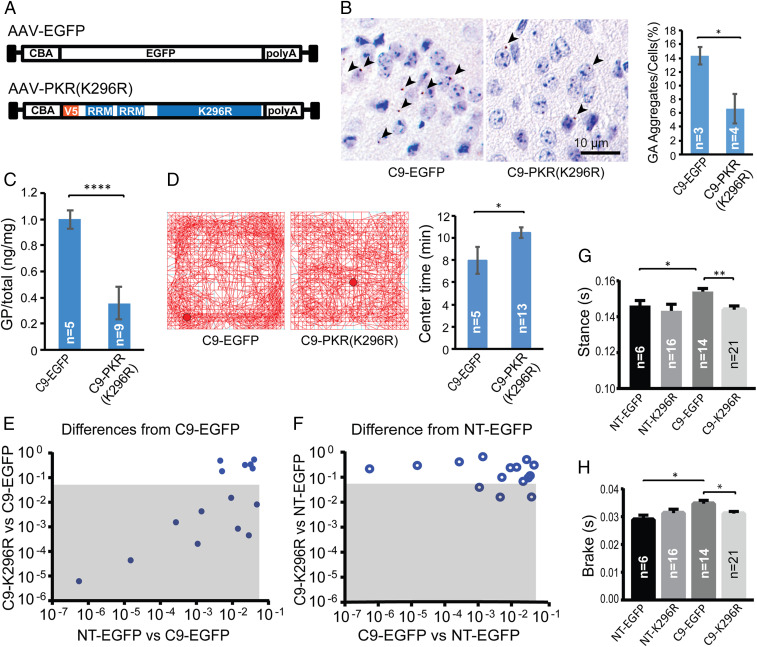
Fig. 3.
Inhibition of PKR decreases RAN proteins and improves behavior in C9-BAC mice. (A) Schematic diagrams of EGFP control and PKR-K296R AAV2/9 constructs used for ICV injections of C9-BAC and NT mice. (B) Representative IHC staining (brown color) of GA RAN protein aggregates in retrosplenial cortex from C9-EGFP and C9-PKR-K296R mice with quantification of GA RAN protein aggregates. Two-tailed t test; *P < 0.05, Bars show ± SEM. (C) MSD assay of brain lysates showing PKR-K296R–treated mice have lower levels of soluble GP RAN protein. Bars show ± SEM. (D) Open-field analyses of C9 mice treated with PKR-K296R or EGFP. (E and F) Comparisons of C9-relevant DigiGait parameters among AAV PKR-K296R and EGFP treatment cohorts at 3 mo of age. Gray boxes show parameters that significantly differ between PKR-K296R C9 and EGFP C9 cohorts (E) or PKR-K296R C9 and NT EGFP cohorts (F). (G and H) Example DigiGait data for Stance and Brake parameters. Statistical analyses were performed using two-tailed t tests (B–D), *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001 with corrections for multiple comparisons in G and H, *P < 0.025, **P < 0.005. Bars show ± SEM. All analyses were done in a blinded fashion.