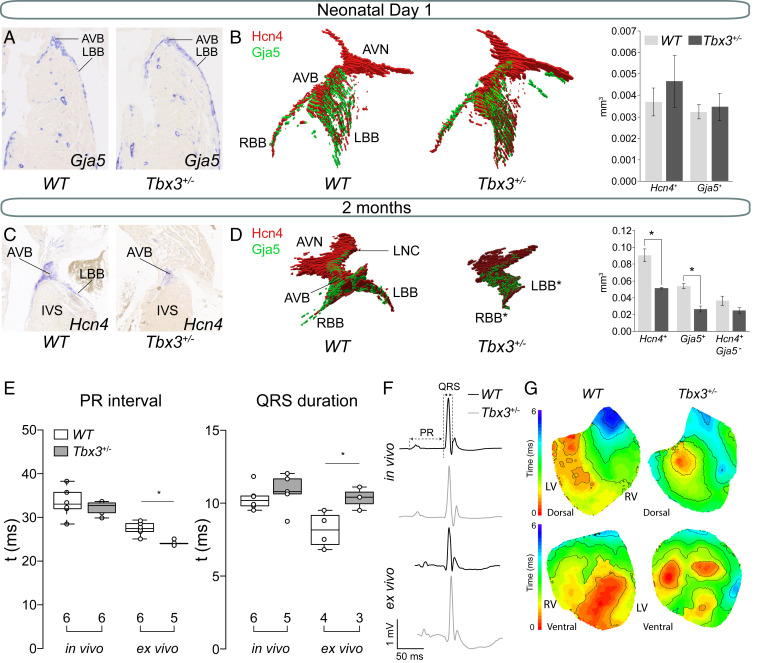
Fig. 1.
Hypoplasia of the AV bundle-bundle branches and conduction disturbances in adult Tbx3+/− mice. (A) Representative sections of newborn WT and Tbx3+/− AVB-BBs. (B) Examples of a reconstruction of newborn WT and Tbx3+/− AV conduction system showing expression of Hcn4 (red) and Gja5 (green). Average volumes of Hcn4 (AV conduction system) and Gja5 (AV bundle and bundle branches) and Hcn4+-Gja5+ (AV node) expression domains in the AV conduction system of three WT (dark gray) and three Tbx3+/− (light gray) mice. Error bars represent SEM. *P < 0.05 was considered significant using a two-tailed Student’s t test. (C) Representative sections of 2-mo-old WT and Tbx3+/− AVB-BBs. (D) Example of a reconstruction of WT AV conduction system showing expression of Hcn4 (red) and Gja5 (green). Average volumes of Hcn4+, Gja5+, and Hcn4+-Gja5− expression domains in the AV conduction system of three WT (dark gray) and three Tbx3+/− (light gray) mice. Error bars represent SEM. (E) Boxplots visualizing the individually measured and average PR interval and QRS duration in vivo and ex vivo. Numbers below boxplot reflect the number of animals measured. (E) Boxplots visualizing the individually measured and average PR interval and QRS duration in vivo and ex vivo. (F) In vivo and ex vivo ECG traces from WT and Tbx3+/− mice. (G) Dorsal and ventral activation maps from WT and Tbx3+/− mice based on optical mapping. *P < 0.05 was considered significant using two-way ANOVA. AVB, atrioventricular bundle; AVN, atrioventricular node; IVS, interventricular septum; LBB, left bundle branch; LNC, lower nodal cells; RBB, right bundle branch.