Figure 1.
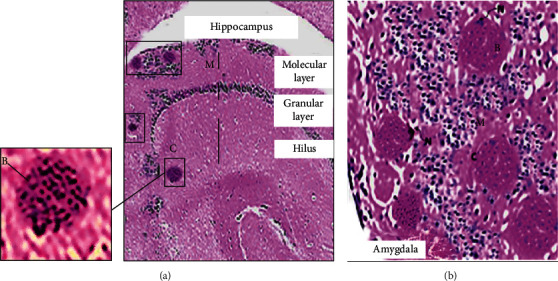
Hematoxylin and eosin stain where the plate reflects the cerebral lesions of T. gondii in the chronically infected Swiss albino mice. (a) Hippocampus with scattered variable-sized bradyzoites encased in cysts (C) in the hilus layer and the molecular layer (M) of the ventral hippocampus (40x). (b) Amygdala lodged with hundreds of bradyzoites (B) in cysts (note the basophilic dot-like terminal nuclei of the parasite) encased in the intracellular cysts (C) (note the lateral nucleus of the host cell (N)) surrounded by mononuclear chronic inflammatory infiltrates (M) (200x).
