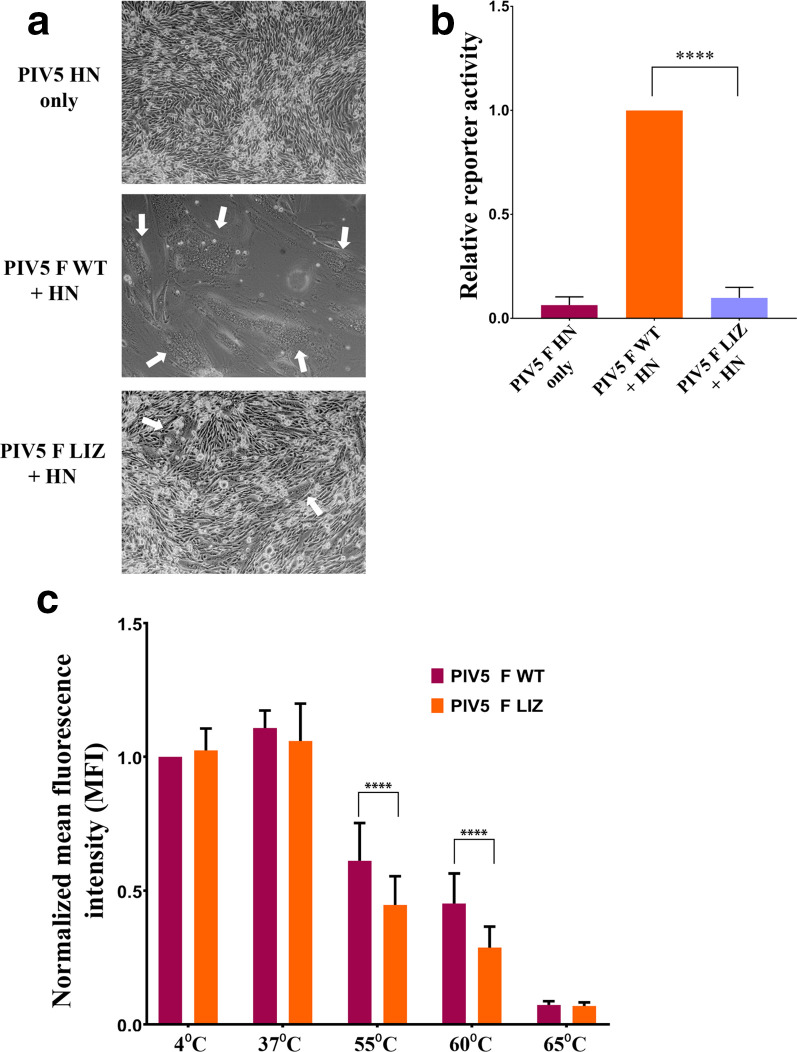
Fig. 3.
Mutations to the L/I zipper of PIV5 reduce F-mediated fusion activity. (a). Syncytia assay. BHK cells plated in six-well plates were transfected with 2.5 µg of total DNA with the PIV5 HN attachment protein alone, PIV5 WT F and HN or PIV5 LIZ F and HN. Syncytia formation was analysed 24 h post-transfection. Images were taken with a Nikon TS100 microscope. White arrows indicate syncytia. Images are representative of two independent experiments, each carried out in triplicate. (b). Luciferase reporter gene assay to quantify F fusogenic activity. Vero cells in 24-well plates were transfected with 1.0 µg total DNA with a T7 promoter plasmid and PIV5 F WT+HN or pIV5 F LIZ+HN. The following day, Vero cells were overlaid with BSR cells and incubated for 3 h to allow for luciferase production. Luciferase activity was measured using a luciferase assay system. The average represents three independent experiments, each performed in duplicate. (c). Thermal triggering assay to observe PIV5 F WT and LIZ pre-fusion thermostability. Cells expressing surface PIV5 F or WT were exposed to 4, 37, 55, 60 or 65 °C for 15 min. Cells were immediately placed on ice for 15 min and prepared for flow cytometry using PIV5 mAb F1a. The average represents two independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. The LIZ mutant was compared to WT using a using Student’s t-test. ****P<0.0001