Figure 5.
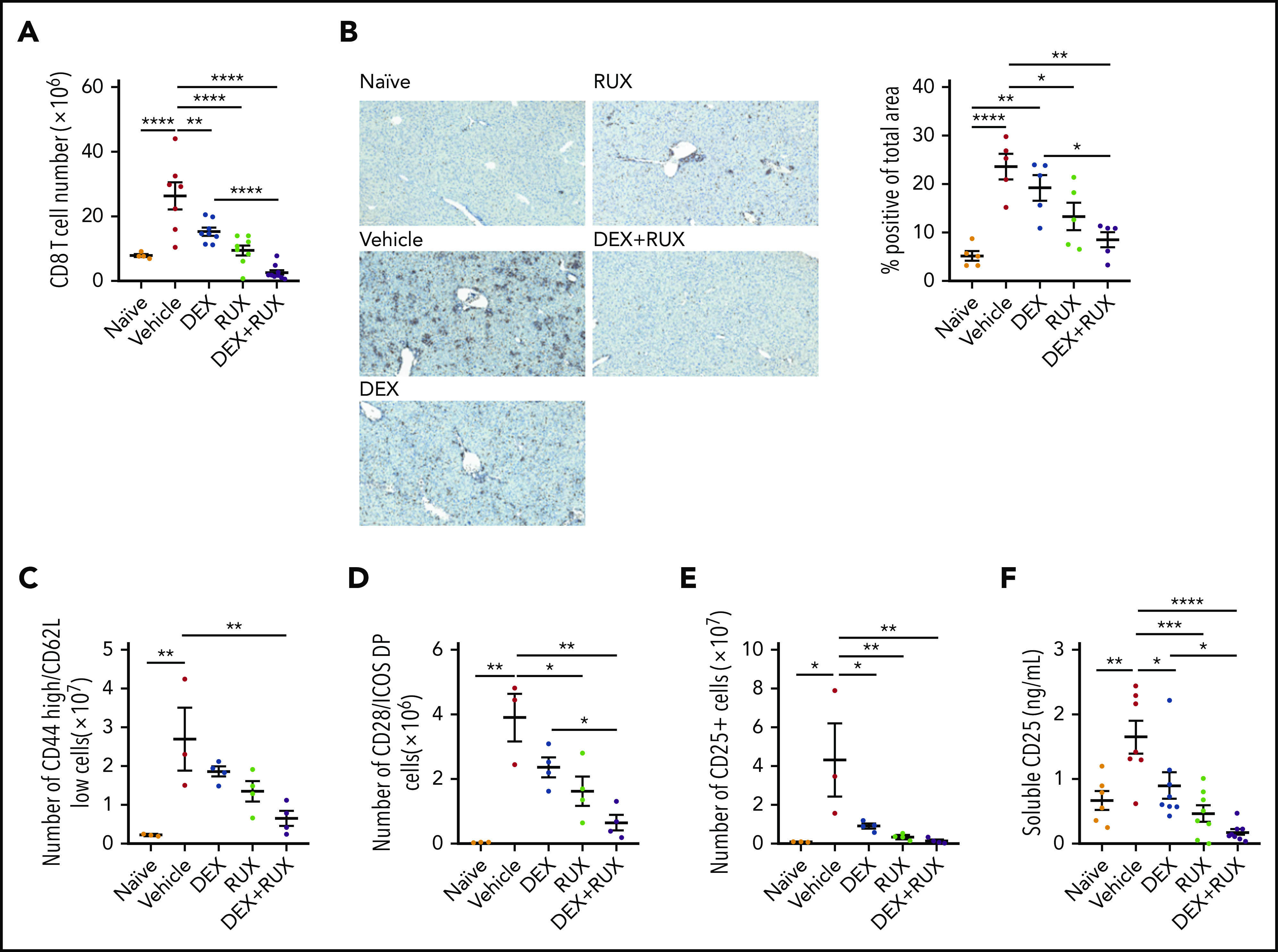
The combination of DEX and RUX cooperatively attenuates CD8 T cell number and markers of CD8 T cell activation in an in vivo model of HLH. (A) Number of splenic CD8 T cells in naïve and vehicle- and drug-treated LCMV-infected mice on day 9 postinfection. (B) Representative histologic images and percentage of total area staining positively for CD3 in livers from naïve and vehicle- and drug-treated LCMV-infected mice on day 9 postinfection. (C) Number of CD44 high/CD62L low cells in spleens from naïve and vehicle- and drug-treated LCMV-infected mice on day 9 postinfection. (D) Number of CD28 and ICOS double-positive cells in spleens from naïve and vehicle- and drug-treated LCMV-infected mice on day 9 postinfection. (E) Number of CD25-positive CD8 T cells in spleens from naïve and vehicle- and drug-treated LCMV-infected mice on day 9 postinfection. (F) Levels of soluble CD25 in plasma from naïve and vehicle- and drug-treated LCMV-infected mice on day 9 postinfection. Statistical significance was assessed using 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s method for multiple comparisons adjustment (A-F). The data in panels A and F represent a combined analysis of 2 independent experiments. ****P < .0001; ***P < .001; **P < .01; *P < .05.
