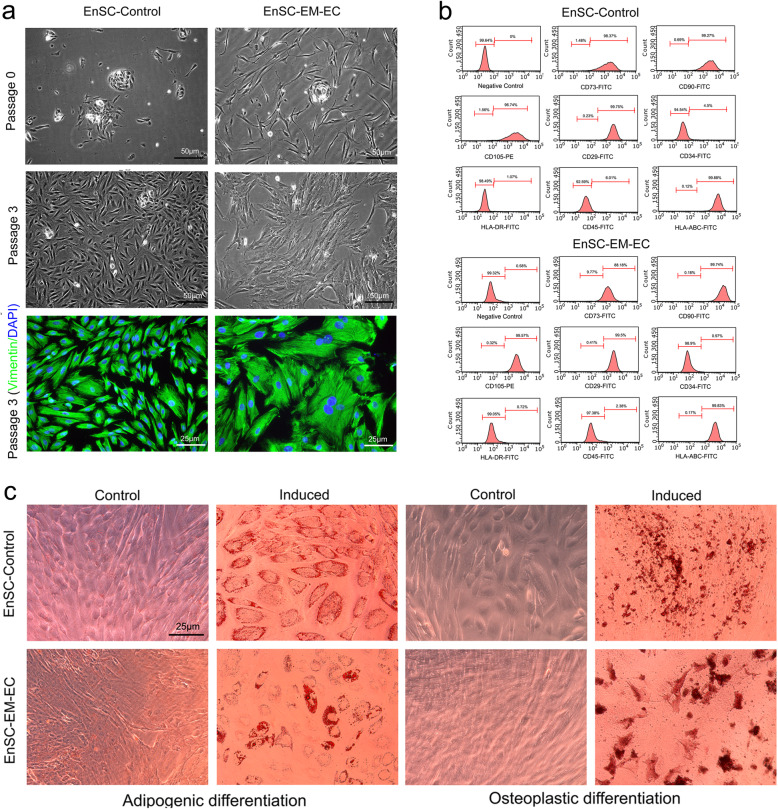
Fig. 1.
Isolation and identification of EnSCs. a Morphology of EnSCs. P0 and P3 EnSC-Control showed a typical spindle-shaped, fibroblast-like morphology with a radial or helical growth pattern, but EnSC-EM-EC showed an irregular morphology instead of a spindle-shaped, fibroblast-like morphology. Furthermore, the expression of vimentin in EnSC-Control and EnSC-EM-EC cells are examined by conventional immunofluorescence. Representative images are shown. b Phenotype of EnSCs. Both EnSC-Control and EnSC-EM-EC were positive for the expression of typical ASC markers (CD29, CD73, CD90 and CD105) and HLA-ABC and negative for the expression of haematopoietic stem cell markers (CD34 and CD45) and HLA-DR. c Conventional adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation were induced, and differentiation was visualized as positive Oil red O and Alizarin red staining. Scale bar, 25 μm