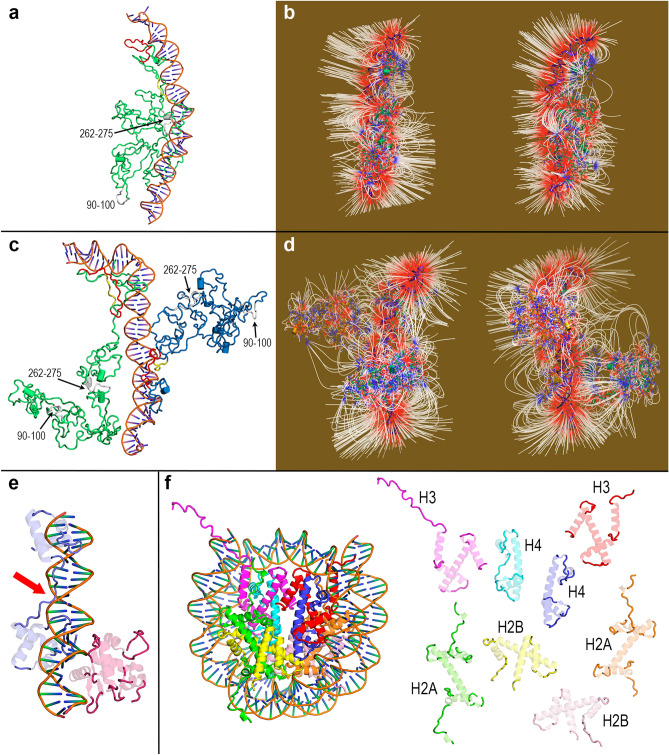
Figure 8.
Final geometries of Dsup-DNA complexes after all-atom MD 100 ns simulations and structural disorder in DNA-binding proteins. (a) Dsup-DNA complex. The conserved sequence regions are marked in the protein ribbon with the same colours used in Fig. 1a. (b) Two views of the electric field E = 7 kT-equivalent units in this final geometry. (c) (Dsup)2-DNA complex. The conserved sequence regions are marked in both protein ribbons (green: DsupA, blue: DsupB) with the same colours used in Fig. 1a. (d) Two views of the electric field E = 7 kT-equivalent units in this final geometry. (e) Disordered regions (opaque loop segments) of the Ets-1 transcription factor (red ribbon) and its paired domain of PAX5 box protein (blue ribbon) increase DNA binding affinity by up to 1,000-fold because of their flexibility (PDB id: 1MDM). The red arrow points to the particularly long disordered segment which adapts to the DNA structure (f) Left: crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle of Xenopus laevis (PDB id: 1AOI). Wrapping DNA encloses two copies of core histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. Right: separate views of the eight histones at the geometry inside the nucleosome particle with same colours and disordered segments shown as opaque ribbons.