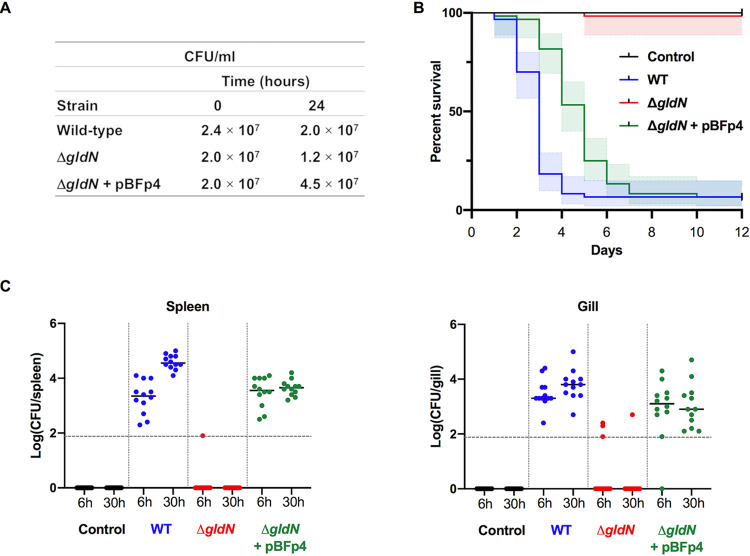
FIG 9.
Analysis of virulence of wild-type and ΔgldN mutant cells toward rainbow trout following immersion challenge. Groups of 42 fish were infected by immersion with F. psychrophilum wild type (WT), ΔgldN mutant, and ΔgldN mutant complemented with pBFp4. The results of two independent experiments are presented. (A) F. psychrophilum bacterial loads in aquarium water during fish infection by immersion. Average results for bacterial quantification determined at the beginning (0 h) and end (24 h) of fish infection challenge. (B) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of rainbow trout after immersion challenge (each group composed of 30 fish). Survival curves for fish challenged with the ΔgldN mutant or with either the wild type or the ΔgldN mutant complemented with pBFp4 are significantly different (Mantel-Cox log rank test, P < 0.0001). Colored shaded areas indicate 95% confidence intervals. (C) Bacterial loads in organs of rainbow trout after immersion challenge. Six fish were sacrificed at 6 h and 30 h postinfection for each group. Serial dilutions of homogenized organs were incubated on TYESG agar supplemented with fetal calf serum (50 ml/liter) to determine the CFU. Bacterial loads of spleen (left) and gills (right) are shown. Horizontal dashed line indicates the detection threshold. Values are significantly lower for the ΔgldN mutant than for wild-type and complemented strains (Mann-Whitney P < 0.0001).