Figure 4.
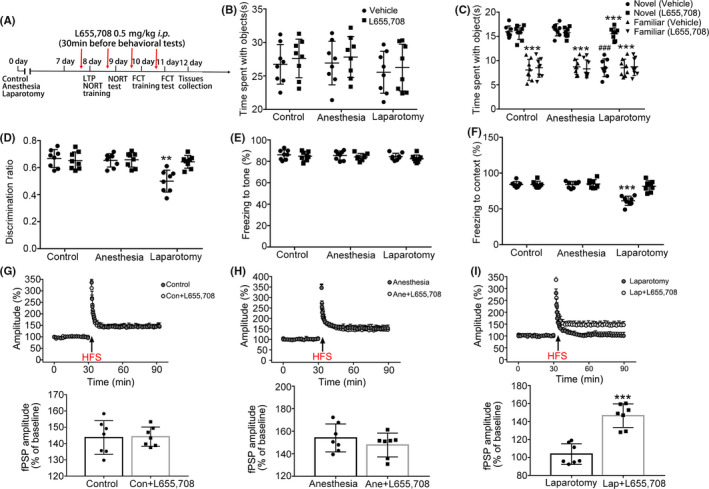
L655,708 could reverse anesthesia and surgery induced learning and memory deficits in aged mice. A, The diagram shows the process of the experiment. The time points of L655,708 (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle administered are marked by the red arrow. Samples were taken at the end of the experiment. B‐D, In the NORT, the time spent with objects was similar among the three groups, while the time spent with a novel object and the discrimination ratio were increased in the laparotomy mice after using L655,708 (n = 8). E‐F, In the FCT, there was no difference in the tone freezing time after using L655,708. However, the freezing scores for memory of context were increased in the laparotomy mice after using L655,708 (n = 8). G‐I, The amplitude of fPSPs in the laparotomy group was increased after using L655,708, while there was no difference in the control and anesthesia mice (n = 7). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. **P < .01, ***P < .001, ### P < .001
