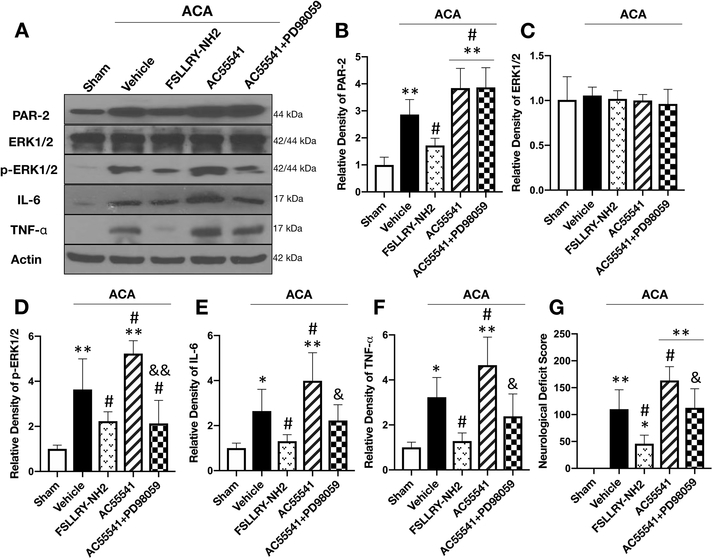
Fig. 5:
Inhibition of ERK1/2 abolished the neuroinflammatory effect of PAR-2 activation at 24 hours after ACA.
Representative Western blot images (A) and quantitative analysis of PAR-2 (B), ERK1/2 (C), p-ERK1/2 (D), IL-6 (E) and TNF- α (F) in the brain revealed increased protein levels at 24 hours following ACA except for ERK1/2 compared to the Sham group. Treatment with FSLLRY-NH2 significantly reduced p-ERK1/2 and proinflammatory cytokine levels compared to the ACA + vehicle group. Further activation of PAR-2 with AC55541 only aggravated the neuroinflammatory response by increasing p-ERK1/2 expression. Potent ERK1/2 inhibitor PD98059 reversed the neuroinflammatory effect of AC55541. Neurologic outcome assessment with NDS at 24 hours following ACA (G) revealed that the inhibition of PAR-2 significantly improved neurologic function while AC55541 alone significantly worsened performance compared to the ACA + vehicle group. This detrimental effect of AC55541 on NDS was reversed by the ERK1/2 inhibitor, PD98059. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. n= 6/group. ANOVA, Tukey. **p<0.001 vs. Sham group, *p<0.05 vs. Sham group, #p<0.05 vs. ACA + vehicle group, &&p<0.001 compared to ACA + AC55541 group, &p<0.05 compared to ACA + AC55541 group.
ACA: asphyxial cardiac arrest