Figure 3. Viral targeting of nuclear neurons in mouse models of temporal lobe and absence epilepsy.
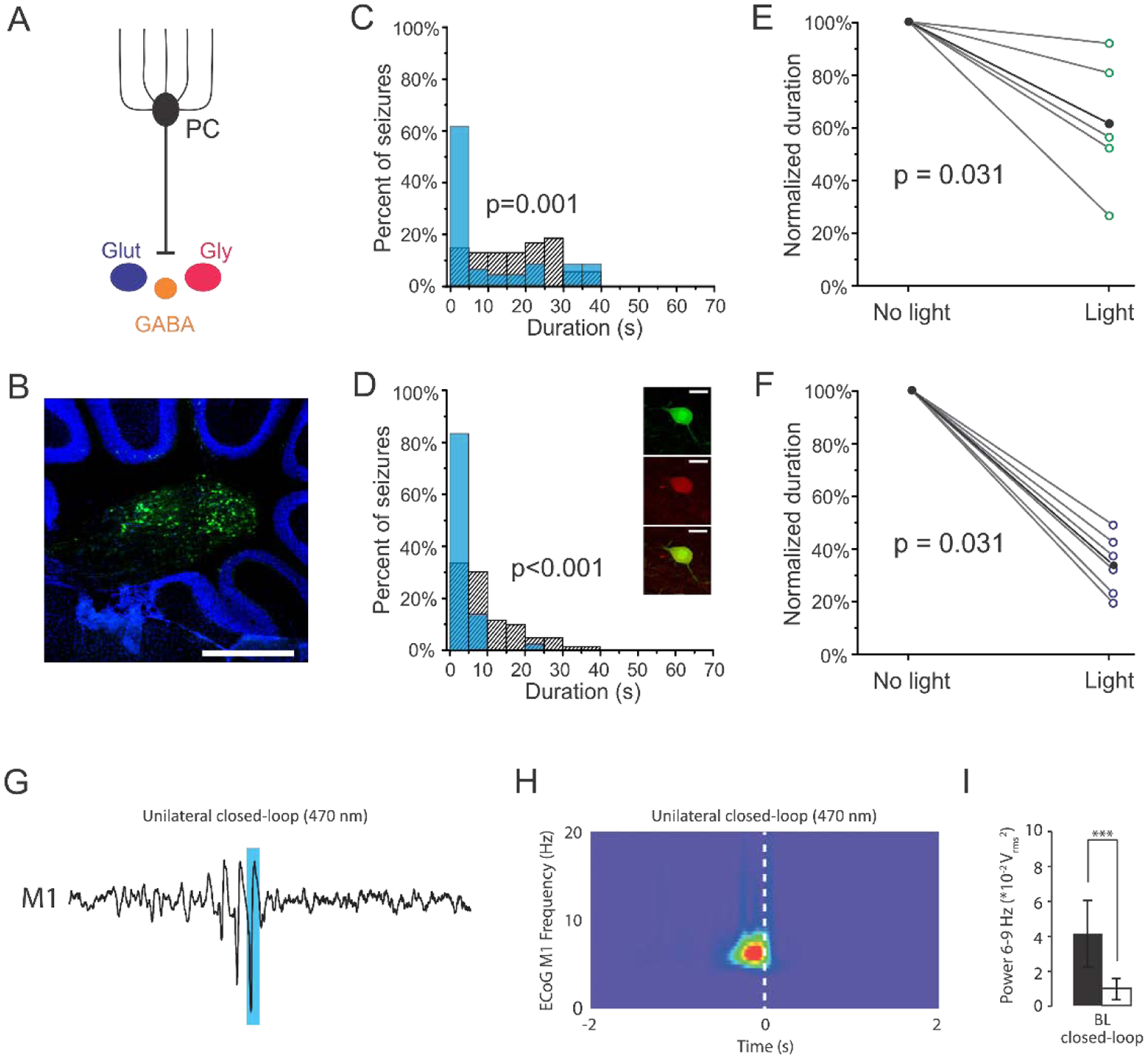
A) Viral approaches allowed for broadly targeting nuclear neurons or selective targeting of glutamatergic nuclear neurons (dark blue). B) GFP expression in nuclear neurons following injection of cre-dependent virus in a VGluT2-cre mouse. Scale bar: 500μm. C) Post-detection seizure durations for an example animal, illustrating that light delivery significantly reduces seizure duration when virally targeting the fastigial nucleus broadly (in this example, a 44% reduction, p = 0.001, two sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). Blue bars: events receiving light intervention; hashed bars: no-light internal controls. D) Seizure inhibition is also achieved by selectively targeting glutamatergic nuclear neurons (in this example, an 81% reduction, p < 0.001, two sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). Inset: Immunocytochemistry confirmed selective expression in glutamatergic neurons following injection of cre-dependent virus in VGluT2-cre animals (Top- green: GFP, middle- red: VGluT2 immunohistochemistry, Bottom- overlay. Scale bar: 70μm.) E-F) Selective targeting of glutamatergic neurons in the fastigial nucleus (F) produces significantly greater seizure attenuation than targeting fastigial neurons more broadly (E; broad targeting versus selective targeting: p = 0.026, Mann-Whitney). Each open circle represents one animal; black data points represent mean. G) Closed-loop optogenetic excitation of the deep cerebellar nuclei (targeting all nuclear neurons broadly using a viral approach) attenuates generalized spike and wave discharges in primary motor cortex in the C3H/HeOuJ mouse model. Blue bar indicates timing of light delivery. H) Wavelet spectrogram of the electrocorticograph during closed-loop stimulation, showing cessation of the GSWD event was time-locked to the onset (dashed bar) of intervention. I) Closed-loop intervention significantly reduces motor cortex band power associated with the GSWDs (p < 0.05, repeated measures ANCOVA). Panels A-F reproduced with modification and permission from [126]. Panels G-I reproduced with permission from [66].
