Fig. 2.
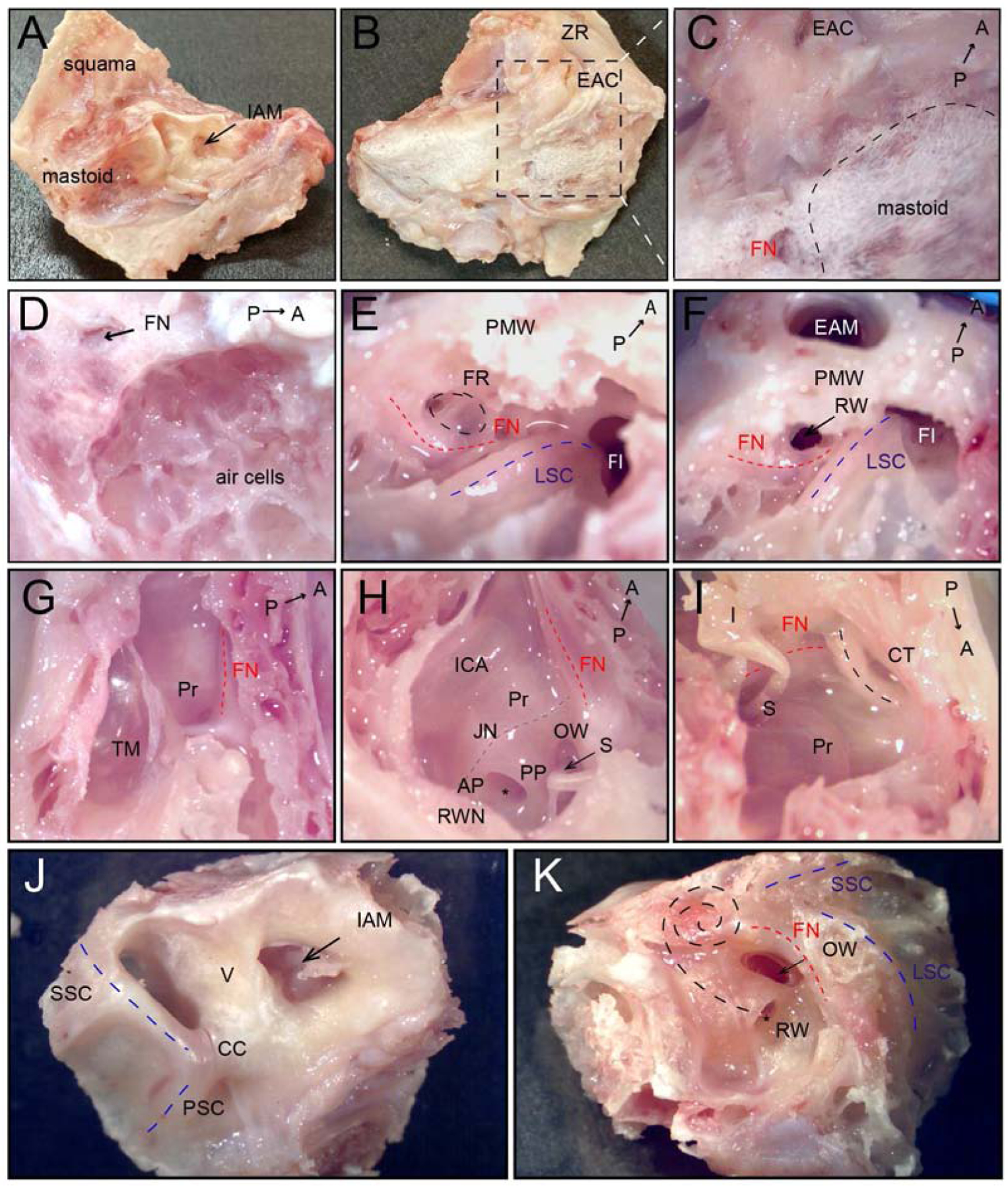
Dissection and visualization of anatomical structures of the middle and inner ear in a cynomolgus monkey left temporal bone. A) Medial surface of the temporal bone, arrow indicates internal auditory meatus. B) Lateral surface of the temporal bone after removal of postauricular muscles. C) High magnification of mastoid region (black dashed line). D) After cortical mastoidectomy; air cells are identified. E) Approach to facial recess in the mastoid; facial nerve—red dashed line, facial recess—black dashed line, lateral semicircular canal—blue dashed line. F) Facial recess opened to access the RW; arrow points to RW. G) Tegmental wall removed, view from the top. H) Lateral and tegmental walls removed, view from posterior to anterior; Jacobson nerve with inferior tympanic artery—grey dashed line. I) Lateral and tegmental walls removed, view from anterior to posterior; black dashed line—chorda tympani nerve. J) Medial surface of the cochlea and the vestibular of inner ear; blue dashed lines—posterior and superior semicircular canal, arrow indicates internal auditory meatus. K) The lateral surface of the cochlea and the vestibular of inner ear; black dashed lines indicate the projection of cochlear turns. A, anterior; AP, anterior pillar; CC, common crus, CT, Chorda tympany; EAC, external auditory canal; EAM, external auditory meatus; FI, fossa incudis; FN, facial nerve (red dashed line); FR, facial recess (black dashed line); I, incus; IAM, internal auditory meatus; ICA, internal carotid artery; JN, Jacobson nerve with inferior tympanic artery; LSC, lateral semicircular canal (blue dashed line); OW, oval window, P, posterior; PMW, posterior meatal wall, PSC, posterior semicircular canal (black dashed line); PP, posterior pillar; Pr, promontory; RW, round window; RWN, round window niche; S, stapes; SSC, superior semicircular canal (black dashed line); TM, tympanic membrane, V, vestibule; ZR, zygomatic root.
