Fig 4.
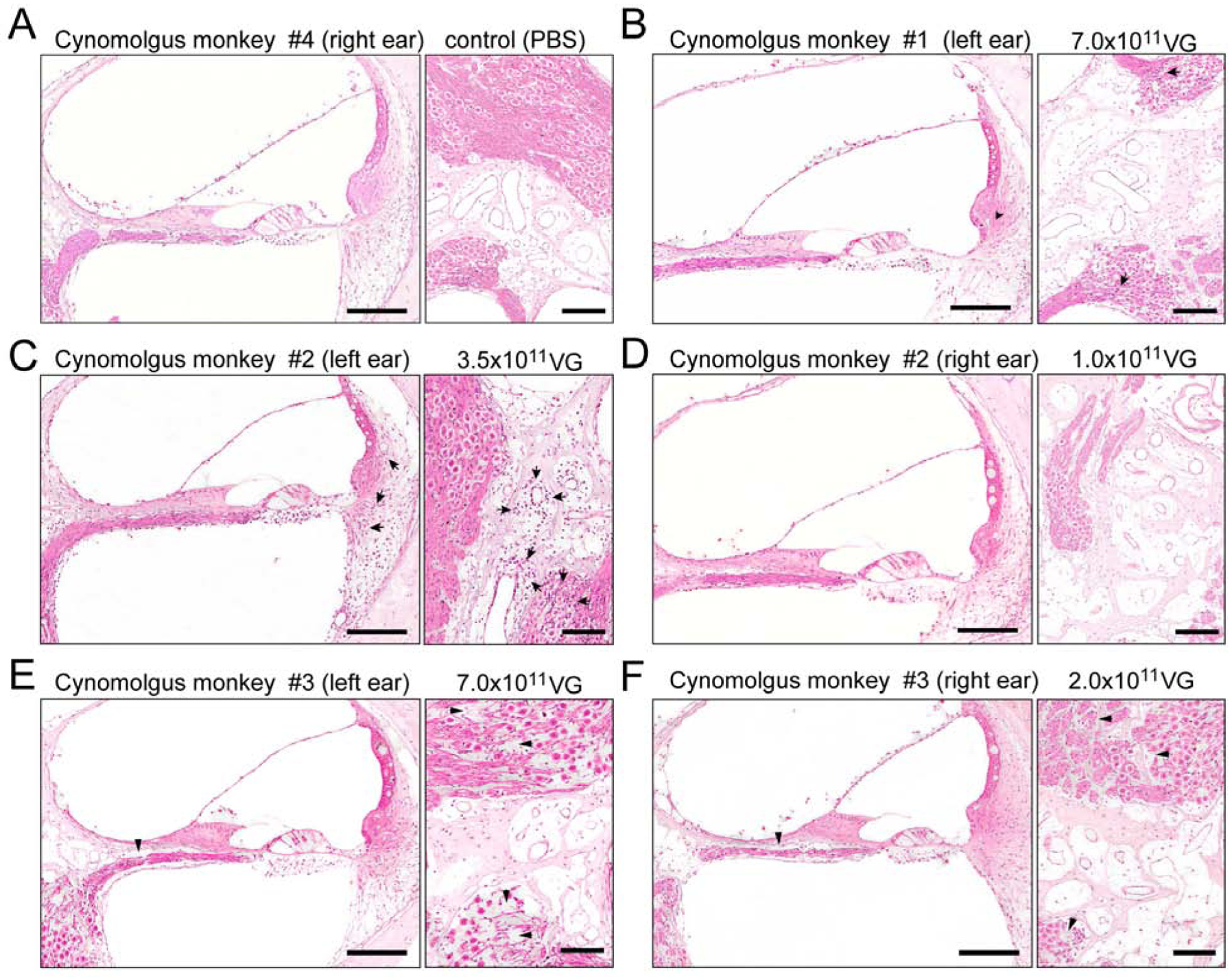
Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the injected ears of cynomolgus monkeys administered with 1×1011 VG, 2×1011 VG, 3.5×1011 VG, and 7.0×1011 VG of AAV9-PHP.B-CBA-GFP, respectively. A) Cynomolgus monkey #4. The right ear, injected with PBS (10 μl), shows no indication of immune infiltration in the organ of Corti, lateral wall (left panel) or spiral ganglion region (right panel). B) Cynomolgus monkey #1. The left ear (7.0 × 1011 VG; 20 μl) shows minimal focal perivascular mononuclear cell infiltration (arrows) in the spiral ligament (left panel) and in the spiral ganglion region (right panel). C) Cynomolgus monkey #2. The left ear (3.5 × 1011 VG; 10 μl) shows perivascular mild multifocal mononuclear cell infiltrates (mostly lymphocytes) in spiral ligament (left panel) and in the spiral ganglion region, mostly perivascular (arrows). D) Cynomolgus monkey #2. The right ear (1.0 × 1011 VG; 10 μl) shows no indication of immune infiltration in the organ of Corti, lateral wall (left panel) or spiral ganglion region (right panel). E) Cynomolgus monkey #3. The left ear (7.0 × 1011 VG; 20 μl) shows loss of nerve fibers and spiral ganglion neurons in the basal turn of the cochlea (right panel, arrowheads) and no indication of immune response in the organ of Corti or lateral wall (left panel). F) Cynomolgus monkey #3. The right ear (2.0 × 1011 VG; 10 μl), shows loss of nerve fibers and spiral ganglion neurons in the basal turn of the cochlea (right panel, arrowheads) and no indication of immune response in the organ of Corti or lateral wall (left panel). Scale bar 150 μm.
