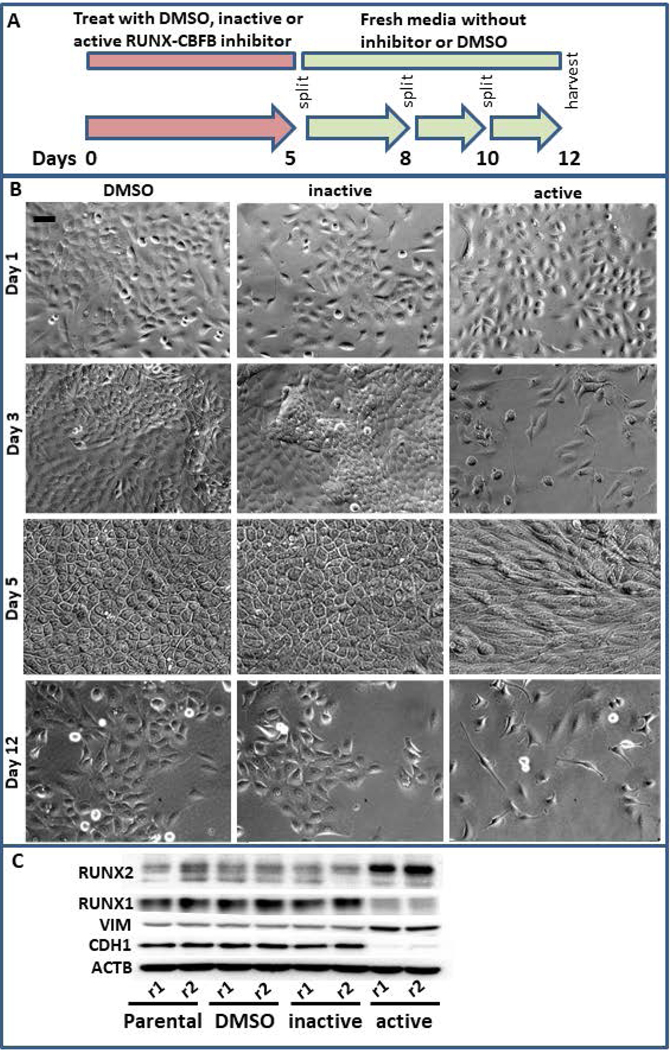
Figure 5.
Simultaneous RUNX1 and RUNX2 inhibition results in epithelial to mesenchymal transition. (a) MCF10AT1 were treated for 5 days with DMSO, an inhibitor that interferes with the interaction between CBFβ and RUNX factors, or an inactive version of this inhibitor that is chemically similar but does not interfere with these interactions. These were then allowed to recover for 7 days in fresh media and passaged as normal. (b) This treatment regimen results in slowed cell growth, cell death, and a more mesenchymal-like morphology. Bar in the upper left panel indicates 20 μm. (c) Western blot analysis demonstrates that the resulting cells are higher in RUNX2 and lower in RUNX1 and are more mesenchymal in their expression of CDH1 and VIM. CBFβ, core binding factor β; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; RUNX, Runt-related transcription factor