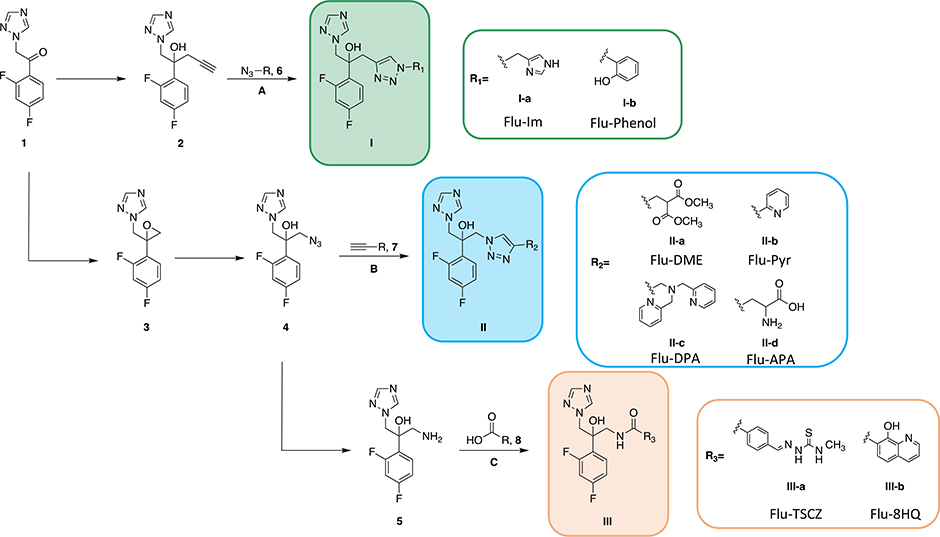
Scheme 1. Synthesis of fluconazole analogues.
Commercially available ketone 1 was converted to alkyne-bearing fluconazole structure 2, which was then reacted with azide-bearing side arm 6 via CuAAC (route A) to obtain compounds with structure I. Alternatively, the ketone was converted to epoxide 3 via a Corey-Chaykovsky reaction. Epoxide 3 then underwent a ring-opening reaction with sodium azide to give azide-bearing fluconazole structure 4. Azide 4 then underwent CuAAC (route B) with alkyne-bearing side arm 7 to afford analogues with structure II or was reduced to the corresponding amine (5) via Pd/C catalyzed hydrogenation. Amine 5 was coupled to carboxylic acid-bearing side arm 8 via HBTU- or EEDQ-mediated coupling (route C) to yield analogues with structure III.