Figure 1.
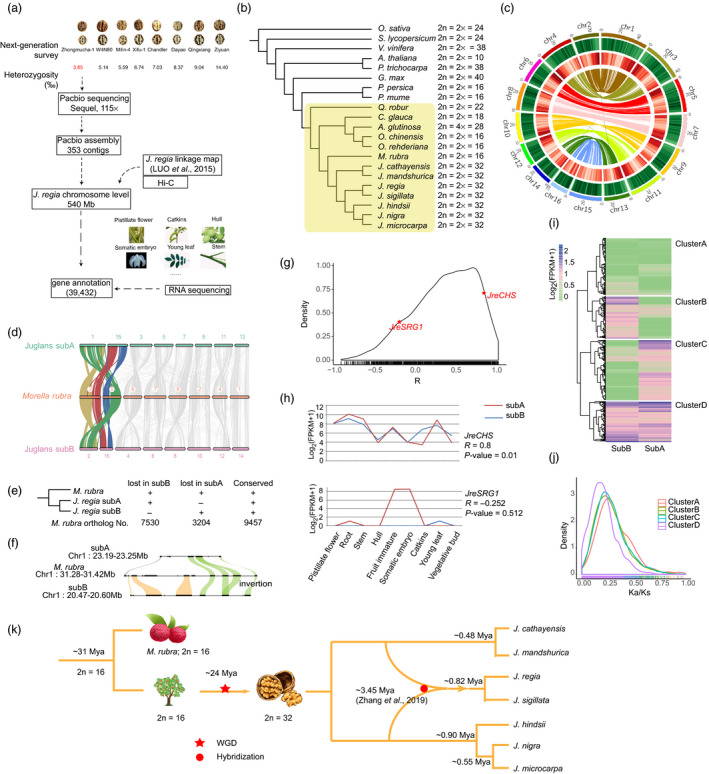
(a) Sequence assembly flow chart for Juglans regia ‘Zhongmucha‐1’. (b) Phylogenetic tree of angiosperm species on the basis of orthologs of single‐copy gene families. Yellow rectangle region represents fagales species. (c) Self‐alignment of walnut genomes. The circus map shows, from outside to inside, ideograms of the sixteen chromosomes, density of TE, density of genes and syntenic blocks. (d) Collinear relationship at the chromosome level between Morella rubra and Juglans regia sub‐genomes. (e) The summary of gene losses in two sub‐genomes of J. regia through comparisons with M. rubra. ‘+’ and ‘‐’ indicate the gene retention and gene loss, respectively. (f) A local comparison for genes in Morella rubra and their orthologs in J. regia sub‐genomes. The black boxes indicate genes, the grey arc ligature indicates gene lost in J. regia subB, the yellow arc ligatures indicate genes lost in J. regia subA, and the green arc ligatures indicate genes conserved in J. regia subA and subB. (g) Expression correlation of sub‐genome paired genes. Frequency distributions are shown for Spearman correlation coefficient calculated from expressions of paired genes in nine tissues. Among them, (h) the detailed expression profiles in nine tissues are shown for JreCHS and JreSRG1. (i) Heatmap and cluster of gene pairs between sub‐genomes based on their expressions in fruit immature. (j) Frequency distributions of Ka/Ks values for four clusters. (k) A summarized model proposed for the phylogeny of Juglans. The divergence time of M. rubra and J. regia was estimated ~ 31 Mya. The walnut genome had undergone a whole‐genome duplication event from 2n = 16 to 2n = 32 chromosomes around 24 million years ago. The rediploidization event was likely to occur soon after WGD for the Juglans genus. J. regia and its landrace J. sigillata arose as a hybrid between the American and the Asian lineages around 3.45 million years ago.
