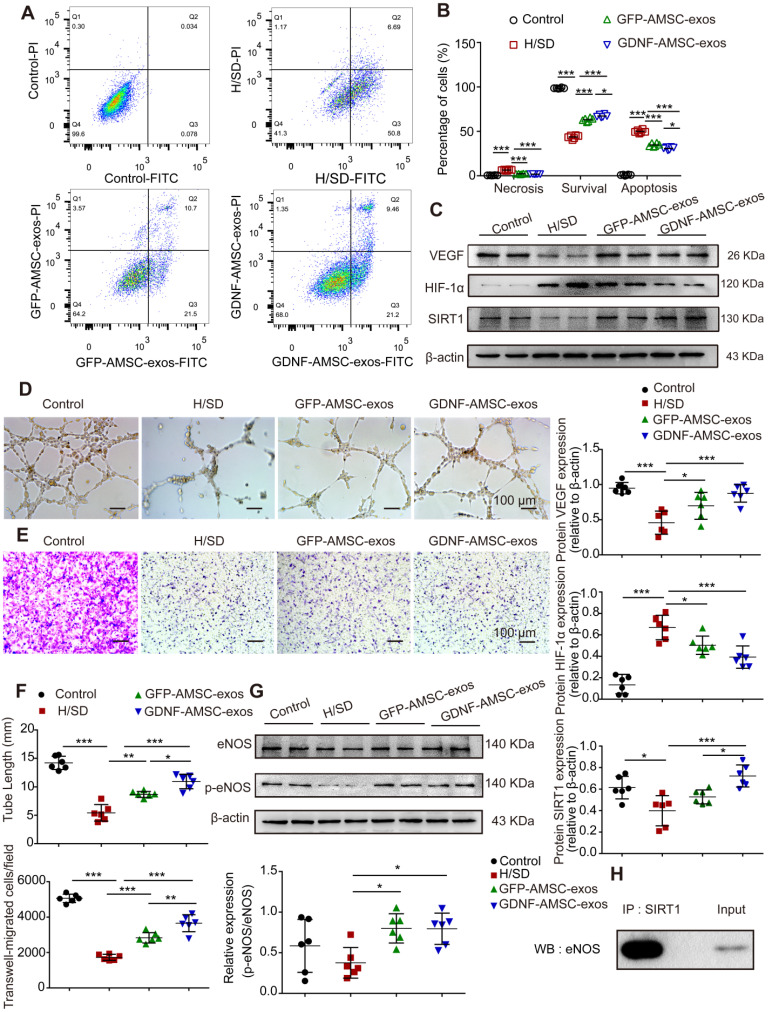
Figure 6.
Exosomes derived from GDNF-modified human adipose mesenchymal stem cells (GDNF-AMSC-exos) promote the migration and tube formation of endothelial cells subjected to hypoxia/serum deprivation (H/SD). (A and B) Cell apoptosis was examined by Annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide (PI) staining using flow cytometry. (C) Representative Western blot image of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) protein expression in endothelial cells. β-actin was used as the loading control. (D and F) Representative images and quantification of human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) tube formation in different treatment groups. Scale bar: 100 µm. (E and F) The migratory ability of HUVECs receiving different treatments was further confirmed by a Transwell assay. Scale bar: 100 µm. Quantitative analysis of the migrated cells in (D). N = 6 per group. (G) The levels of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and phosphorylated eNOS (p-eNOS) in HUVECs receiving different treatments were examined by Western blotting and quantified by densitometric analysis. β-Actin was used as the loading control. (H) Co-immunoprecipitation of endogenous eNOS and sirtuin-1 (SITR1) from HUVECs. Whole-cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-SIRT1 antibodies. Immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with anti-eNOS antibodies. The results are expressed as the means ± SEMs of three different experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.