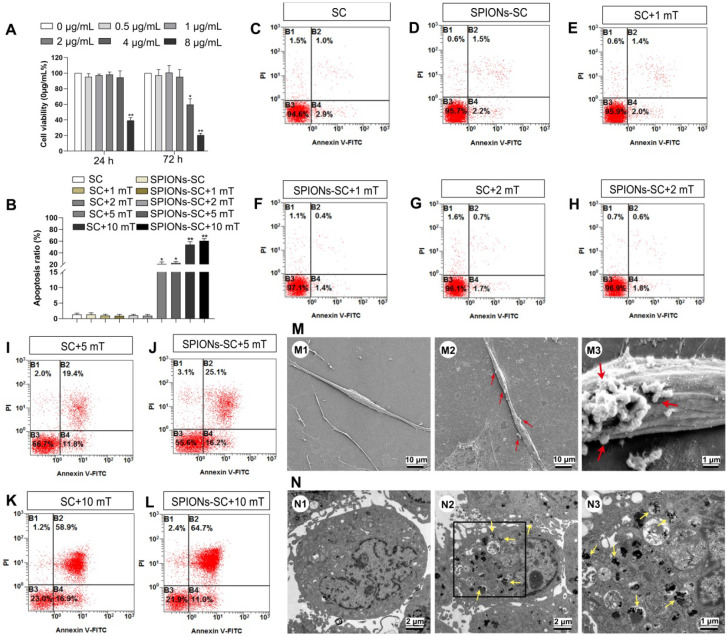
Figure 1.
Cytotoxicity and apoptosis of SCs and cellular localization of SPIONs. (A) Effect of different concentrations of SPIONs on cell viability was examined by CCK-8 assay (n=3) (B) Percentage of apoptotic cells at different MF intensities was evaluated by flow cytometry (n=3) (C) SC cultures (D) SC cultures with 2 μg/mL SPIONs (E) SC cultures +MF group (1 mT) (F) SC cultures with 2 μg/mL SPIONs+MF group (1 mT) (G) SC cultures +MF group (2 mT) (H) SC cultures with 2 μg/mL SPIONs+MF group (2 mT) (I) SC cultures +MF group (5 mT) (J) SC cultures with 2 μg/mL SPIONs+MF group (5 mT) (K) SC cultures +MF group (10 mT) (L) SC cultures with 2 μg/mL SPIONs+MF group (10 mT) (M) Representative SEM images of normal control SCs (M1) and SCs incubated with 2 μg/mL SPIONs for 24 h (M2, M3). The red arrows point SPION agglomerates on the cell membrane. (N) Representative TEM images of normal control SCs (N1) and SCs incubated with 2 μg/mL SPIONs for 24 h (N2). The yellow arrows point SPIONs in the cytoplasm; most retained SPIONs dispersed as single particles. (N3) High magnification of the boxed area in (E). All data are expressed as means±SEM. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test with Tukey's post hoc test was used to examine the significance of results. * P<0.05 and ** P<0.01 for comparison with SCs cultures control group.