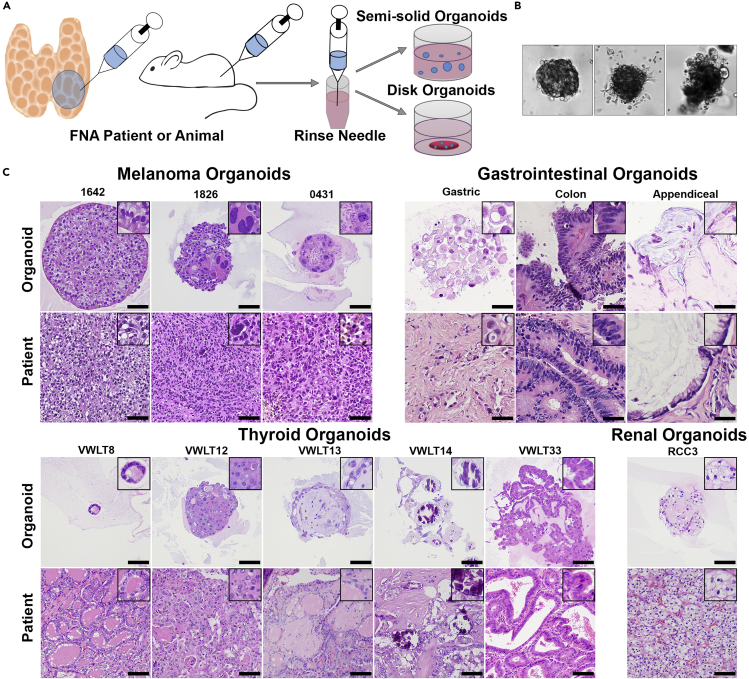
Figure 1.
FNA-Based Patient-Derived Organoid Model
(A) Fine-needle aspiration can be performed on patients, surgical specimens, or animals. One to three needle passes are typically collected, and the needle is rinsed in RPMI 1640 or DMEM. Following this rinse, the cells can be directly plated in either a semisolid or disc organoid format.
(B) Organoids begin to form within 1 week of plating and have morphologies unique to each individual patient. Three melanoma organoids shown have distinct morphology on 20× bright-field imaging.
(C) Organoids can also be embedded in paraffin blocks for morphologic evaluation using H&E staining, images taken at 20× magnification (scale bar, 50 μm). Organoid morphology, as seen on H&E stain, closely recapitulates the primary patient tumor morphology across multiple tumor types including melanoma, gastrointestinal carcinomas, thyroid carcinomas, and renal cell carcinoma.