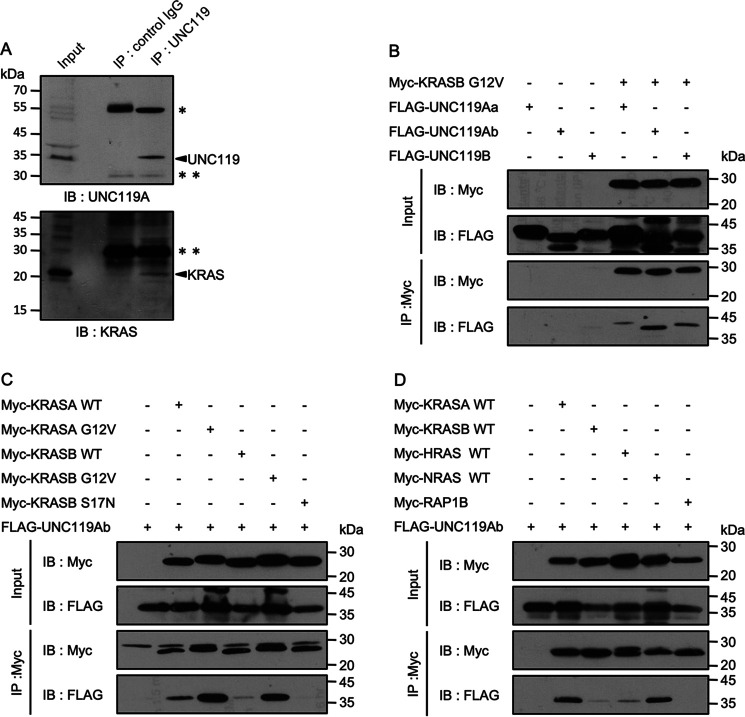
Figure 1.
Interaction between UNC119A and RAS proteins. A, UNC119A was immunoprecipitated (IP) from SW480 cells and immunoblotted (IB) with anti-UNC119 and anti-KRAS antibodies. Single and double asterisks indicate IgG heavy and light chains, respectively. UNC119A and KRAS are indicated with arrows. B, C, and D, Myc-tagged proteins were coexpressed with FLAG-tagged proteins in HEK293FT cells, and 48 h after transfection, immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-Myc antibody. B, pCIneoMyc-KRASB G12V, pCIneoFH-UNC119Aa (FLAG-UNC119Aa), pCIneoFHF-UNC119Ab (FLAG-UNC119Ab), and pCIneoFHF-UNC119B (FLAG-UNC119B) were used. UNC119Aa, UNC119Ab, and UNC119B were coimmunoprecipitated with KRASB G12V. C, pCIneoMyc-KRASA WT, pCIneoMyc-KRASA G12V, pCIneoMyc-KRASB WT, pCIneoMyc-KRASB G12V, pCIneoMyc-KRASB S17N, and pCIneoFHF-UNC119Ab (FLAG-UNC119Ab) were used. KRASA G12V and KRASB G12V more efficiently trapped UNC119Ab than KRASA WT and KRASB WT. KRASB S17N did not bind UNC119Ab (the last lane). D, pCIneoMyc2-KRASA WT, pCIneoMyc2-KRASB WT, pCIneoMyc2-HRAS WT, pCIneoMyc2-NRAS WT, pCIneoMyc2-RAP1B, and pCIneoFHF UNC119Ab (FLAG-UNC119Ab) were used. KRASA and NRAS efficiently bound UNC119Ab compared with KRASB and HRAS. The interaction between UNC119Ab and RAP1B was not detected. Five experiments for panels A and D and three experiments for panels B and C were performed by two members.