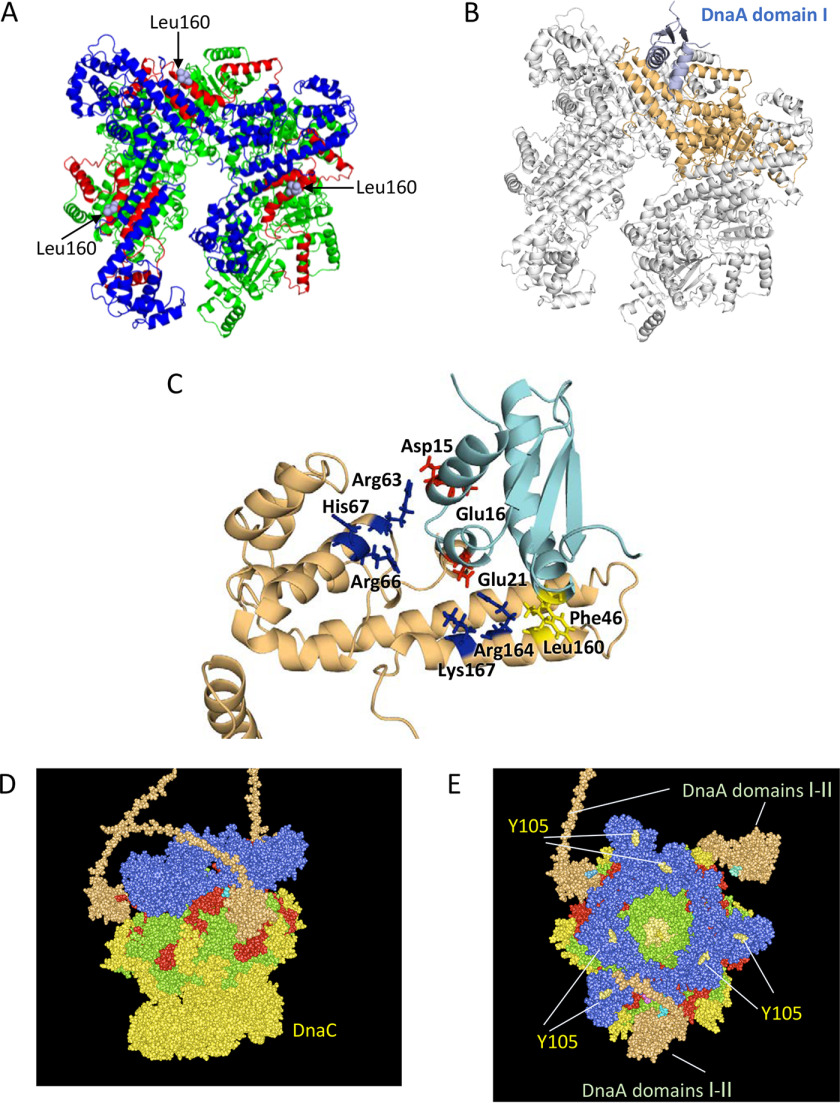
Figure 7.
Structural model for DnaB helicase in complex with DnaA domains I–II. A, ribbon model of a DnaB hexamer structure (PDB code 6QEL) and the positions of Leu160 residues exposed on the surface are shown. DnaB regions are colored as shown in Fig. 1. B, docking model of DnaB and DnaA domain I is shown using a ribbon model. The overall structure with only one DnaA domain I molecule was calculated using the Rosetta server and optimized. DnaA is shown in light blue. DnaB is shown in gray, except for the DnaA-bound protomer, which is shown in brown. C, close-up view of the interface between DnaB and DnaA domains I and II. A part of the docking model (A) is enlarged. DnaB Leu160 and DnaA Phe46 (yellow), DnaA Asp15, Glu16, and Glu21 (red), and DnaB Arg63, Arg66, His67, Arg164, and Lys167 (blue) are shown as stick models. D and E, a possible structure of the DnaA–DnaB–DnaC complex is shown using a space-filling mode. Based on the above and the DnaB–DnaC complex structure (PDB code 6QEM), overall structure of the DnaB–DnaC complex bound to three molecules of DnaA domains I and II (orange) is shown. The DnaB hexamer, which is colored as shown in A, binds six molecules of DnaC (yellow) and three molecules of DnaA domains I and II (orange). An essential DnaG binding site in DnaB, Tyr105, is also shown.