Figure 8.
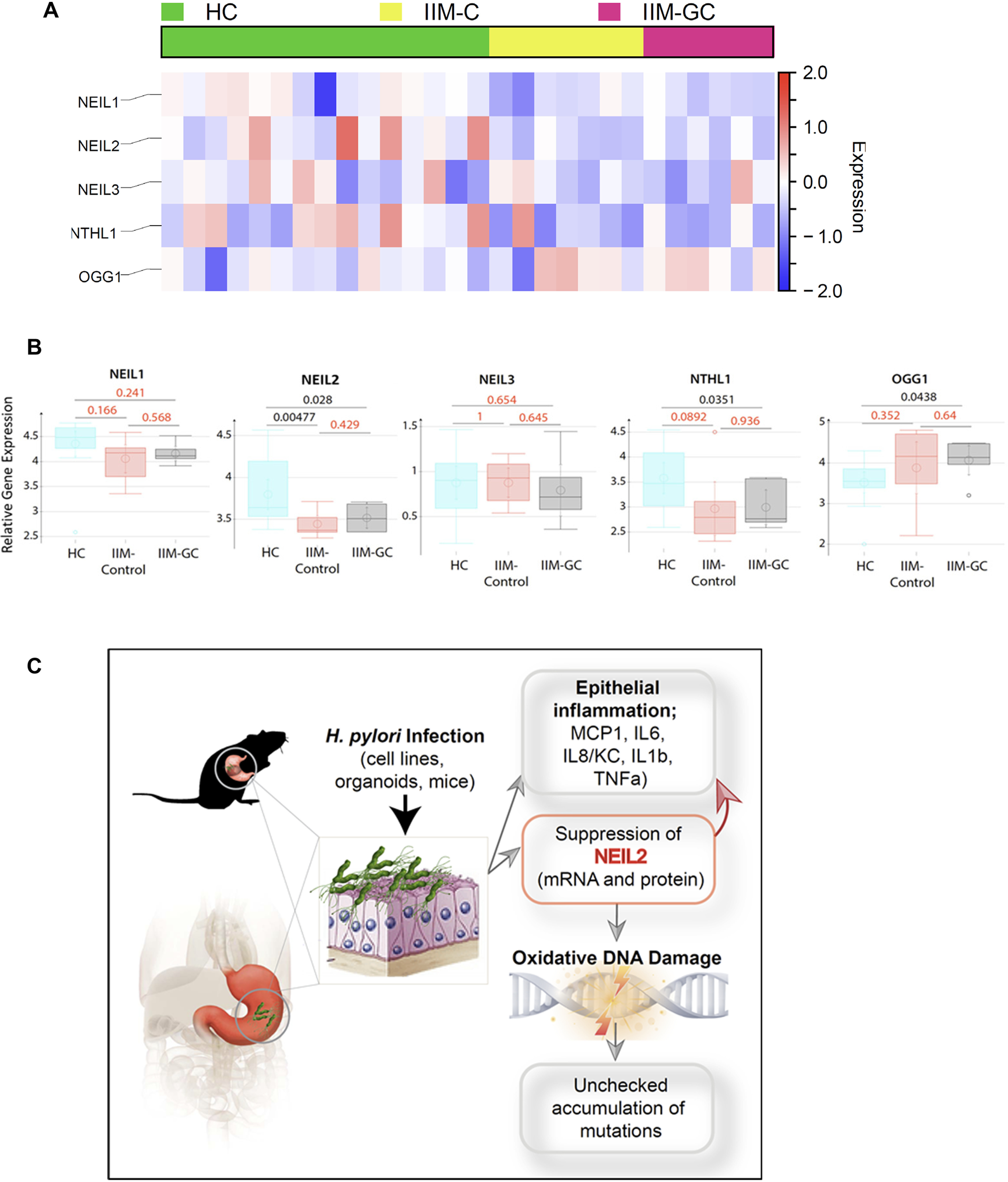
The heat map and the schematic summarize the role of NEIL2 in the initiation of GC. A, a heatmap was generated after analyzing the expression profile of base excision repair genes in the microarray of the publicly available data set (GSE78523) (42). The microarray was performed with the RNA extracted from FFPE cuts of gastric biopsies from a total of 45 human subjects from different disease groups: healthy controls (HC), incomplete metaplasia (IIM-C), and complete metaplasia (IIM-GC). Incomplete metaplasia had a higher progression rate to GC than complete metaplasia. The level of NEIL2 was significantly reduced compared with those of all the genes analyzed in the heatmap. B, NEIL1, NEIL2, NEIL3, OGG1, and NTH1 expression were detected in this cohort. C, H. pylori infection has serious negative effects on the gastric mucosa because of chronic mucosal inflammation leading to DNA damage and downregulation of the base-excision repair protein NEIL2. NEIL2, which actively repairs the damage that occurs during transcription, has impaired repair activity following H. pylori infection and, therefore, accumulates mutations that can lead to GC. D, the schematic diagram summarizes the findings of the current study.
