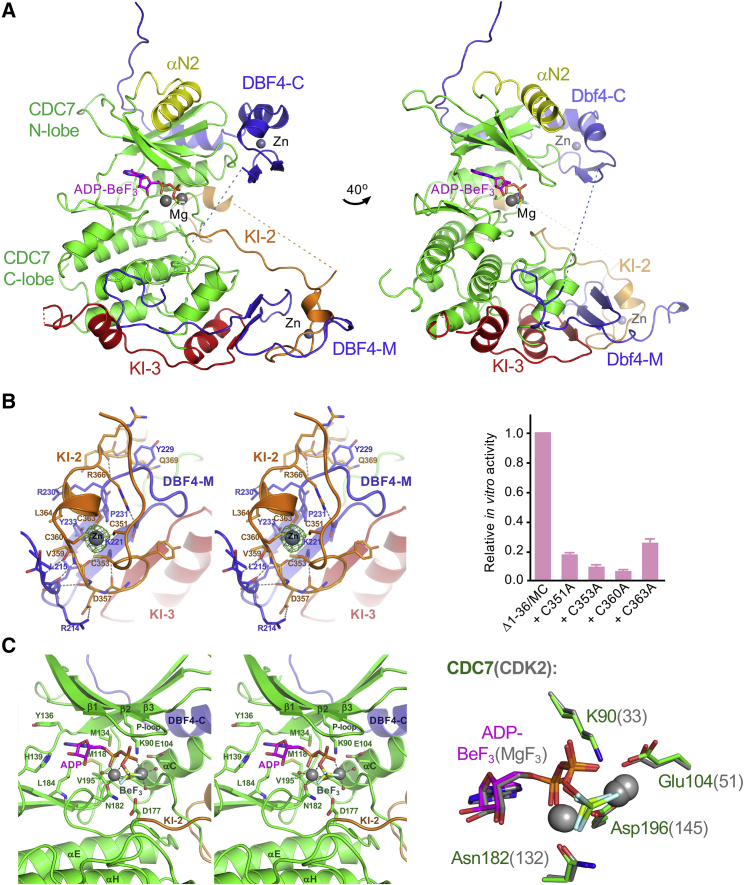
Figure 2.
Crystal Structure of CDC7(Δ1–36/Δ228–345/Δ467–533)-DBF4MC Heterodimer in Complex with ADP-BeF3−
(A) Overview of the structure. Protein chains are shown as cartoons and colored as in Figure 1A, with DBF4 in blue, canonical kinase CDC7 regions in green, and unique elements in yellow (N-terminal region), orange (KI-2), or red (KI-3). Zn and Mg atoms are shown as gray spheres, and nucleotide (ADP-BeF3) as sticks, with carbon atoms in pink and the remaining atoms according to standard conventions: nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, beryllium, and fluoride atoms in blue, red, orange, light green, and gray, respectively. Dotted lines show connectivity, where peptide linkages are disordered in the crystal structure. See Figure S1 for comparison with the structure of the previously reported construct (Hughes et al., 2012).
(B) Left: stereo view of the KI-2 ZF domain and its interactions with DBF4. Selected residues are shown as sticks and indicated. Anomalous difference map calculated from diffraction data acquired using X-rays at the absorption K-edge of Zn (λ = 1.2837 Å) is shown as green mesh, contoured at 5σ; the peak height around the Zn atom is >30σ. Right: relative kinase activities of CDC7(Δ1–36)-DBF4MC constructs without (leftmost bar) and with Ala substitutions of the Zn-coordinating Cys residues.
(C) Left: details of the active site. Final 2Fo-Fc electron density map for the active-site region is shown in Figure S2A. Right: superposition of the active sites of CDC7 and CDK2 (PDB: 3QHW) active sites bound to ATP analogs. Active-site Mg atoms are shown as gray spheres. Nucleotide analogs and selected amino acid residues are shown as sticks and labeled, colored as in (A) (CDC7) or with carbon atoms in gray (CDK2).