Figure 2.
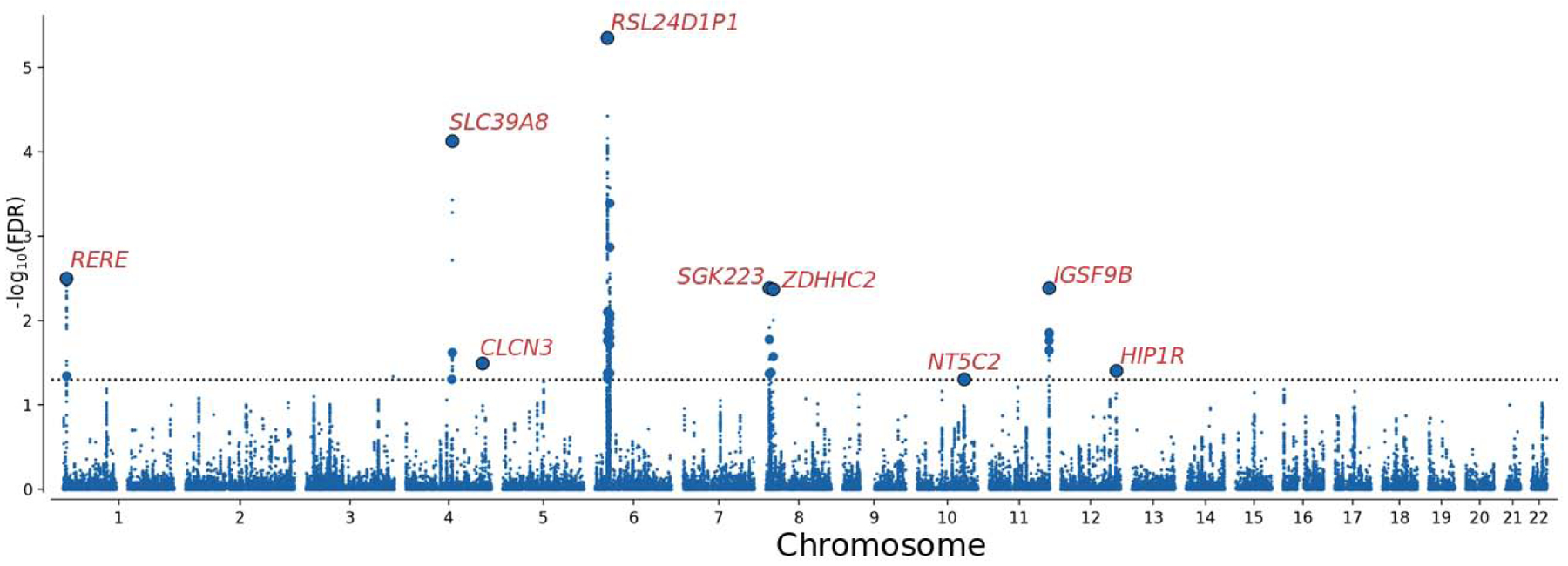
Common genetic variants jointly associated with schizophrenia (n=77,096) and Parkinson’s disease (n=417,508) at conjunctional false discovery rate (conjFDR) < 0.05. Manhattan plot showing the –log10 transformed conjFDR values for each SNP on the y-axis and chromosomal positions along the x-axis. The dotted horizontal line represents the threshold for significant shared associations (conjFDR<0.05, i.e. −log10(conjFDR)>1.3). Independent lead SNPs are encircled in black, and their nearest gene is displayed. The significant shared signals in the major histocompatibility complex region (chr6:25119106–33854733) and region 8p23.1 (chr8:8091701–11835712) are represented by one lead SNP only. Further details are provided in Table 3, and Supplemental Tables 7 and 8.
