Figure 4. The SPAM: hPD-L1 interaction is disrupted by hPD-L1-binding ligands.
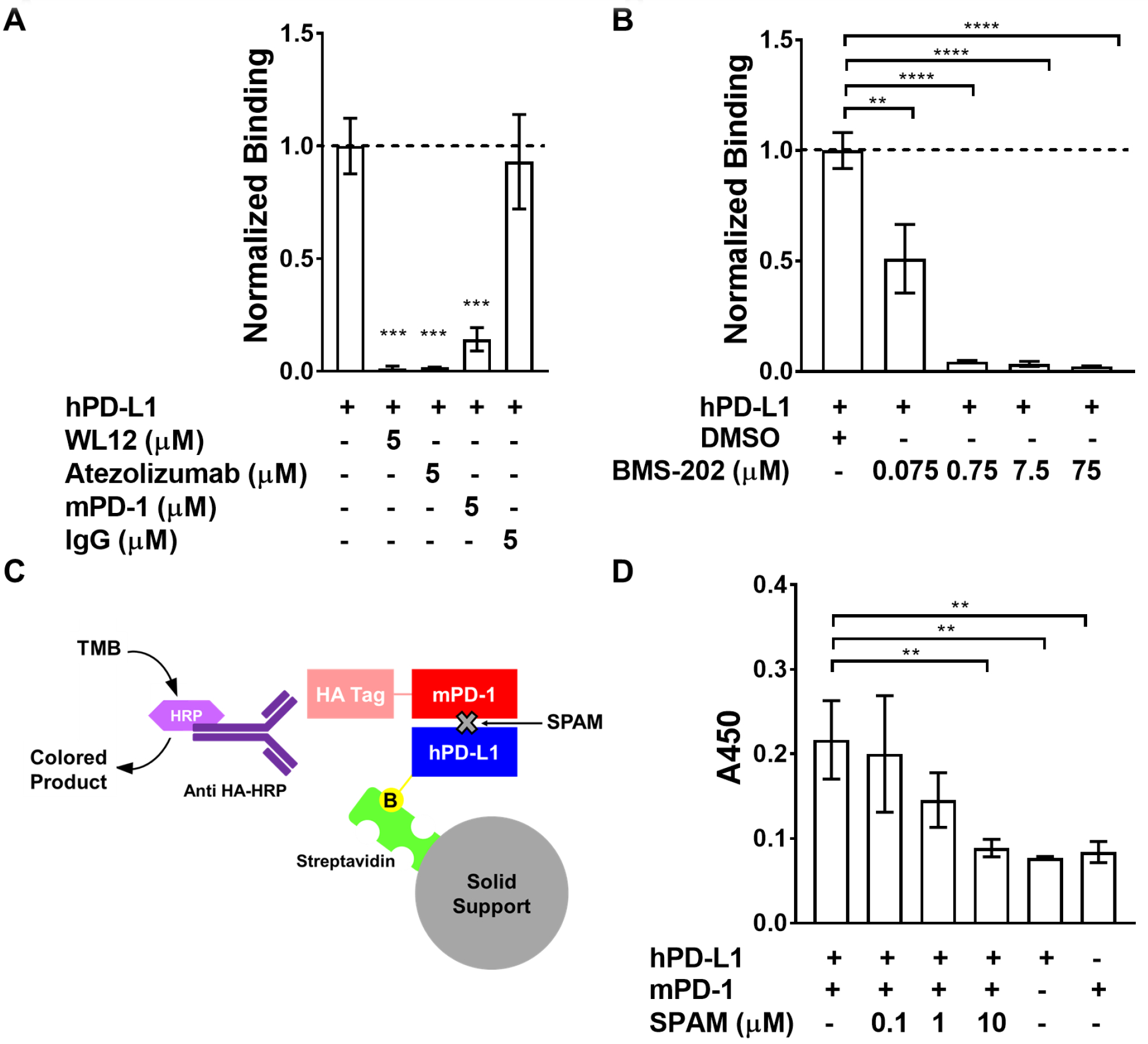
A) [35S]-labeled SPAM binding to immobilized hPD-L1 is disrupted by 5 μM WL12 (p value<0.0001), 5 μM Atezolizumab (p value<0.0001) and 5 μM mPD-1 (p value<0.0001). The presence of 5 μM IgG does not affect SPAM binding to hPD-L1 (p value > 0.05) B) [35S]-SPAM binding to hPD-L1 in the presence of varying concentrations of BMS-202. SPAM binding to hPD-L1 is almost completely inhibited by 750 nM BMS-202 (p value<0.0001). Error bars show the standard deviation of the mean for triplicate measurements. C) Schematic of the hPD-L1/mPD-1 Interaction ELISA/IP assay. D) ELISA/IP assay for hPD-L1 binding to mPD-1 in the presence and absence of different concentrations of SPAM (0.1, 1 and 10 μM). SPAM almost completely inhibits mPD-1 binding at 10 μM (p value <0.01) (Each measurement was carried out in triplicate and error bars show the standard deviation of the mean. Students t-test; p value < 0.05 (*), < 0.01 (**), < 0.005 (***), < 0.001 (****))
