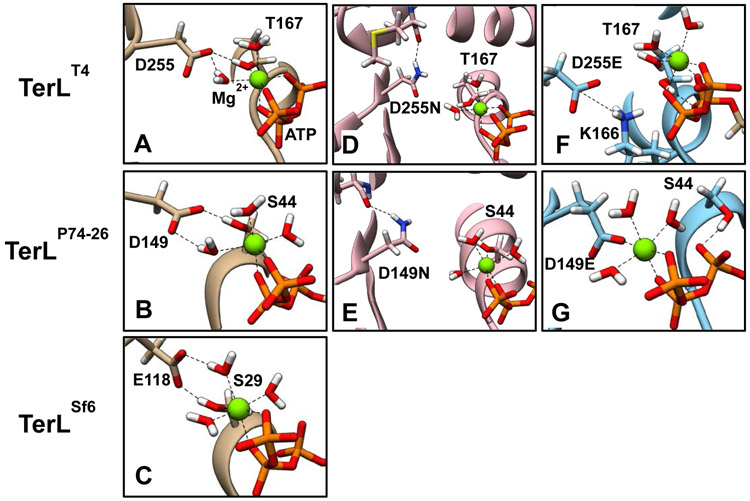
Figure 9. Molecular dynamics simulations identify importance of interaction between WA and WB motifs.
MD simulations of the WT T4 (A), P74-26 (B), and Sf6 (C) terminase proteins highlight a conserved interaction between the WB Asp/Glu carboxylate group and the WA Thr/Ser hydroxyl group. This interaction helps the binding pocket close around the bound Mg2+-ATP as part of the tight binding transition. This interaction is maintained even with the deviant WB Glu found in Sf6 terminase due to a larger backbone-to-backbone distance (see Table 2). Simulations of Asp→Asn variants of the T4 (D) and P74-26 (E) terminase proteins show that these groups remain isolated to the WB motif and do not interact with the WA motif as found in WT. Simulations of the Asp→Glu variants of the T4 (F) and P74-26 (G) terminase proteins suggest unique defects arise in the binding pocket. The simulated T4 mutant D255E interacts with the critical WA K166, similar to mutant crystal structure (see Figure S4). The simulated P74-26 mutant D149E chelates Mg2+ directly as opposed to via a bound water molecule, displacing S44 (compare with panel B).