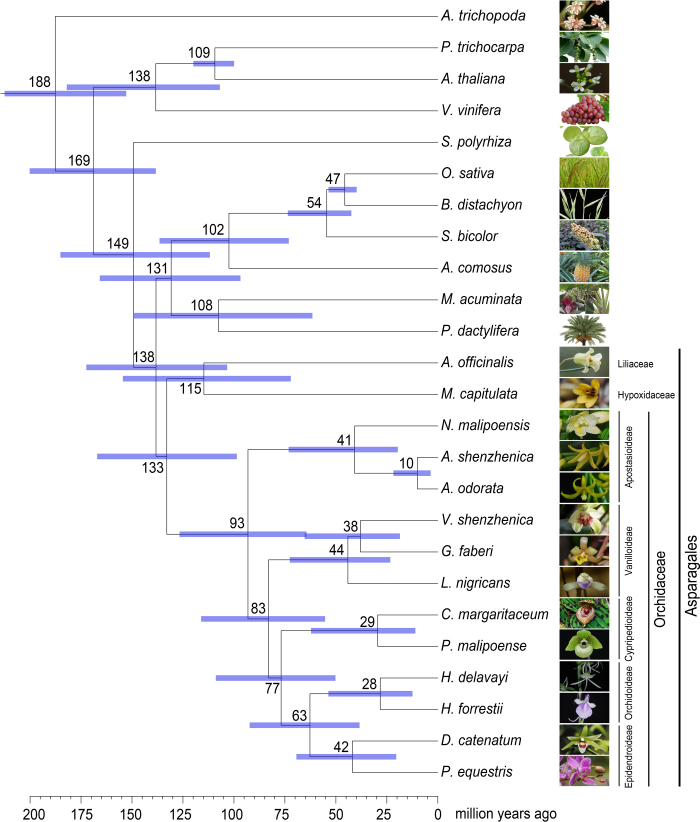
Extended Data Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree showing the topology and divergence times for 15 genomes (A. trichopoda, P. trichocarpa, A. thaliana, V. vinifera, Spirodela polyrhiza, O. sativa, Brachypodium distachyon, Sorghum bicolor, A. comosus, Musa acuminata, Phoenix dactylifera, A. officinalis, A. shenzhenica, P. equestris and D. catenatum) and 10 transcriptomes (Apostasia odorata, Cypripedium margaritaceum, Galeola faberi, Habenaria delavayi, Hemipilia forrestii, Lecanorchis nigricans, M. capitulata, Neuwiedia malipoensis, Paphiopedilum malipoense, Vanilla shenzhenica).
The unigenes of the transcriptomes of the 10 ‘transcriptome’ species were aligned to the 439 single-copy gene families of the 15 ‘genome’ species. One hundred and thirty-two single-copy gene families for the 25 species could be identified, and were used to construct a phylogenetic tree based on the PhyML software61 with the GTR+Γ model, while divergence times (indicated by light blue bars at the internodes) were predicted by MCMCTREE62. The range of the bars indicates the 95% confidence interval of the divergence times.