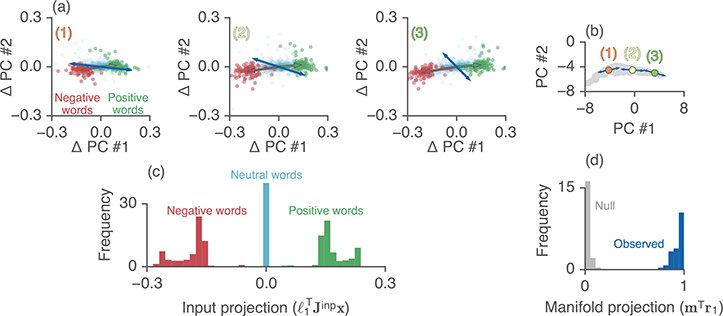
Figure 4:
Effect of different word inputs on the LSTM state vector. (a) Effect of word inputs, Jinpx, for positive, negative, and neutral words (green, red, cyan dots). The green and red arrows point to the center of mass for the positive and negative words, respectively. Blue arrows denote ℓ1, the top left eigenvector. The PCA projection is the same as Fig. 2c, but centered around each fixed point. Each plot denotes a separate fixed point (labeled in panel b). (b) Same plot as in Fig. 2c, with the three example fixed points in (a) highlighted (the rest of the approximate fixed points are shown in grey). Blue arrows denote r1, the top right eigenvector. In all cases r1 is aligned with the orientation of the manifold, m, consistent with an approximate line attractor. (c) Average of the projection of inputs with the left eigenvector over 100 positive (green), negative (red), or neutral (cyan) words. Histogram displays the distribution of this input projection over all fixed points. (d) Distribution of (overlap of the top right eigenvector with the fixed point manifold) over all fixed points. Null distribution consists of randomly generated unit vectors of the same dimension as the hidden state.