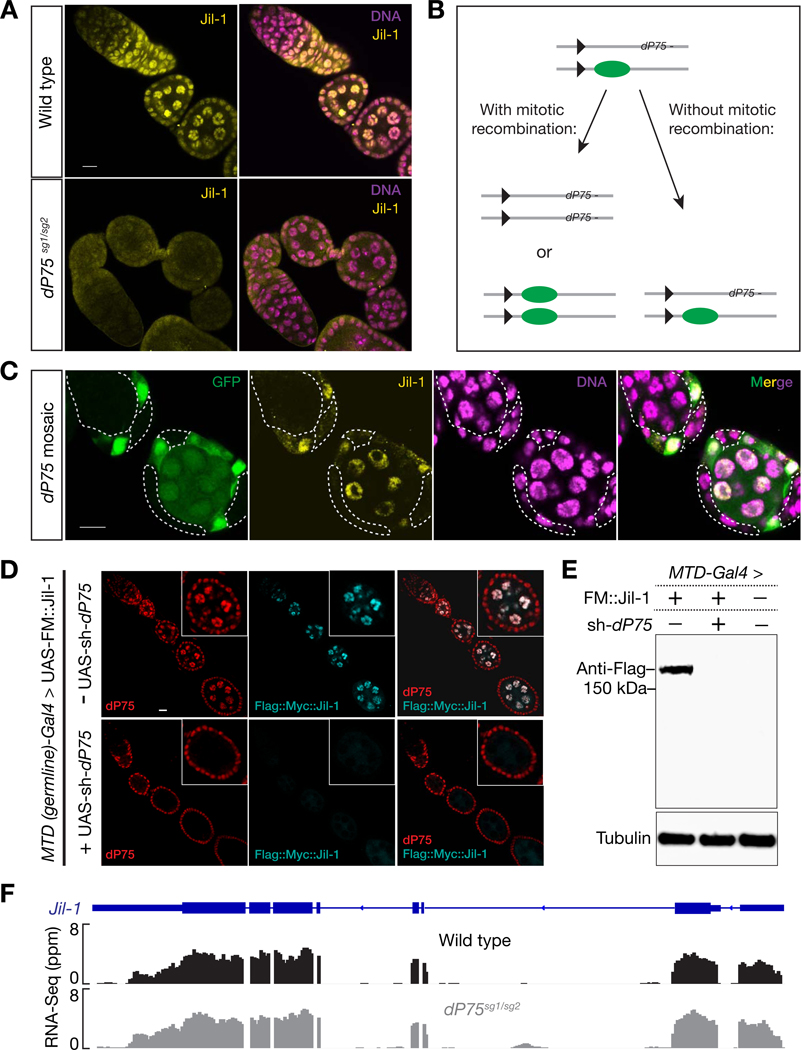
Fig. 4.
dP75 is required for stabilizing Jil-1 protein. A: Immunostaining of Jil-1 in the ovary from either wild-type or dP75 mutants. Jil-1 shows robust nucleus-localized signal in wild-type flies, while these signals are nearly absent in dP75 mutant. B: Strategy for mosaic analysis in (C). C: clonal analysis of Jil-1 expression. dP75 mutant clones were generated through strategy shown in (B) and were subjected to immunostaining with Jil-1 antibody seven days after clone induction. dP75 mutant clones are marked by absence of GFP, and outlined with dashed lines. The detailed method for clone generation is included in Method. D: Immunostaining of transgenic Jil-1 protein in either control or in ovaries with dP75 depleted in germ cells. UAS-Flag::Myc::Jil-1 driven by germline specific Gal4 shows robust expression in wild type ovaries, but is undetectable when dP75 is depleted. E: Western blot for transgenic Jil-1 protein in control and dP75 depleted ovaries. F: RNA-Seq data show that the abundance of jil-1 mRNAs is not affected in dP75 mutants.