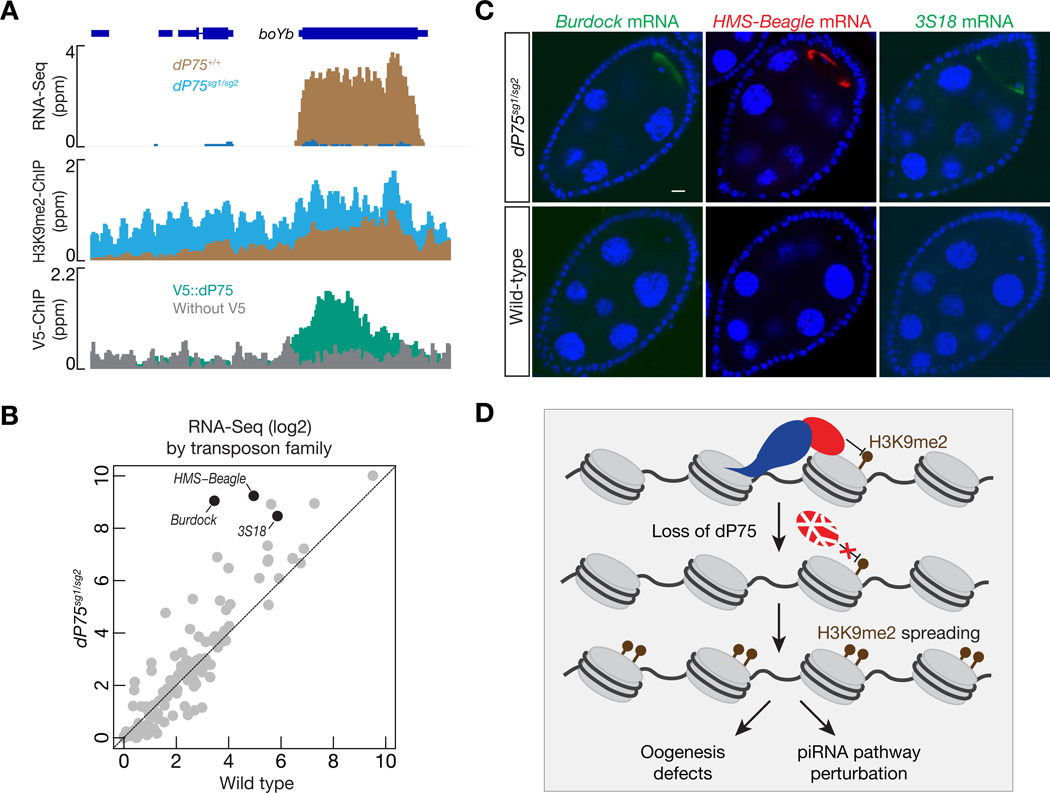
Fig. 7.
dP75 is required for transposon silencing during oogenesis. A: RNA-Seq, V5::dP75 ChIP-Seq, and H3K9me2 ChIP-Seq signals across the boYb gene, which encodes a piRNA pathway component for transposon silencing. dP75 protects boYb from H3K9me2 spreading. B: The change in transposon expression, relative to control, was compared for dP75 mutants. Transposon expression is calculated as FPKM, and both the x-axis and y-axis are in log2 scale. C: RNA FISH to detect the expression and localization of transposon transcripts. D: Graphic model to depict the function of dP75 during oogenesis. dP75 physically interacts with Jil-1, antagonizing the spreading of H3K9me2. Upon loss of dP75, Jil-1 protein is unstable, and leads to H3K9me2 deposition on genes that are required for ensuring oogenesis and transposon silencing.