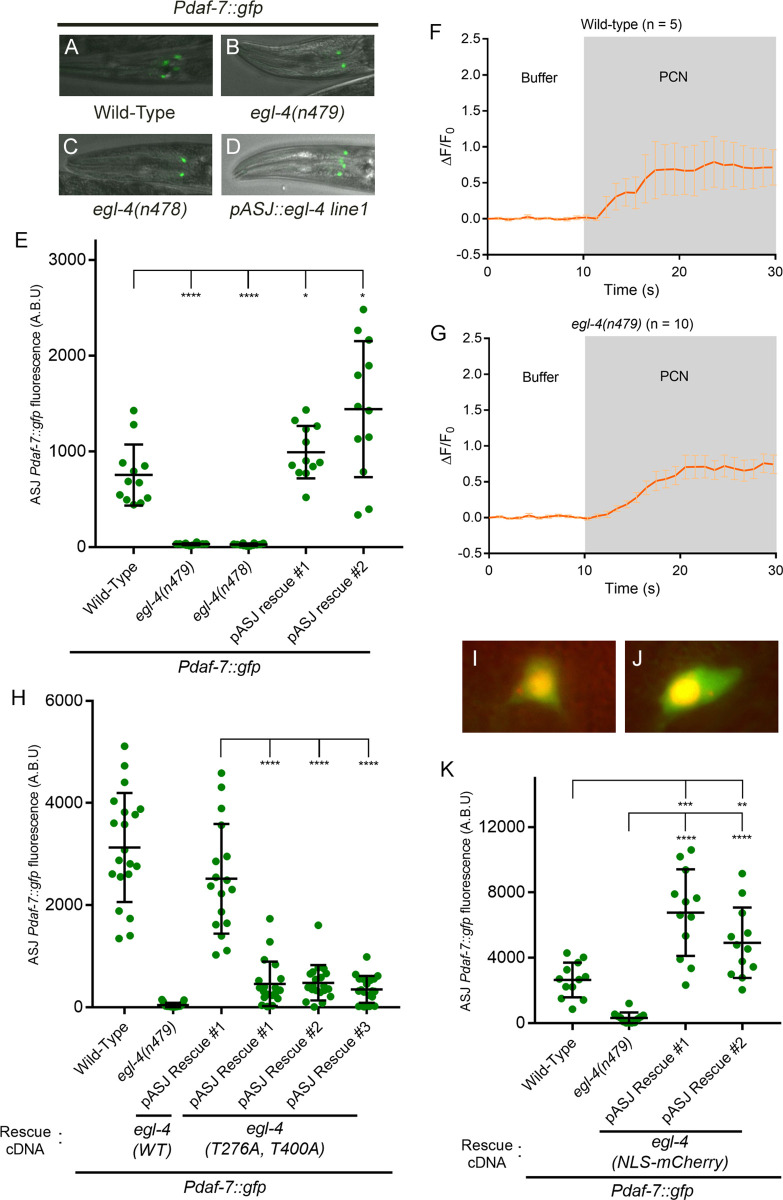
Fig 3. EGL-4 is required in the nucleus for the induction of daf-7 in ASJ neurons upon P. aeruginosa exposure.
(A-D) Pdaf-7::gfp expression after exposure to P. aeruginosa for various egl-4 backgrounds. (E) Maximum fluorescence values of Pdaf-7::gfp in ASJ neurons in various egl-4 mutant backgrounds following P. aeruginosa exposure. Both rescue lines shown have the mutation egl-4(n479) in the background. (F-G) GCaMP5 fluorescence change in the ASJ neurons when exposed to buffer (DMSO) followed by 66 μg/ml phenazine-1-carboxamide (PCN) in wild-type or egl-4 mutants. (H) Maximum fluorescence values of Pdaf-7::gfp in ASJ neurons of egl-4(n479) mutants expressing WT egl-4 cDNA or cGMP-binding defective (T276A, T400A) egl-4 cDNA in the ASJ neurons. (I-J) NLS-mCherry-EGL-4 proteins are localized to the nucleus of ASJ neurons. NLS-mCherry-EGL-4 is seen in the red channels, and GFP from Pdaf-7::gfp is seen in the green channels. GFP is observed throughout the ASJ neurons, outlining the cells. (K) Maximum fluorescence values of Pdaf-7::gfp in ASJ neurons of egl-4(n479) mutants containing the NLS-mCherry-EGL-4 constructs following exposure to P. aeruginosa; the egl-4(n479) column data was from non-transgenic siblings of rescue line #1. Error bars in E, H and K indicate standard deviation, and errors bars in F and G indicate standard errors of the mean. ****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 by Mann-Whitney U test.