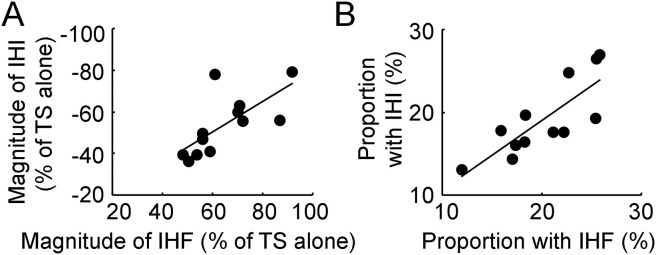
Fig. 4.
Correlation analysis for measurements with interhemispheric interaction. (A) Correlation between IHF and IHI at the peak interstimulus intervals. Abscissa indicates the magnitude of maximal IHF and ordinate indicates the magnitude of maximal IHI. They are expressed as a percentage difference between motor evoked potential amplitude induced by CS-TS paired-pulse stimulation and that induced by TS alone. The value for IHF is positive and that for IHI is negative. (B) Correlation between the proportion of the largest group of transcallosal fibers measured with IHF and that measured with IHI. Abscissa indicates the proportion of transcallosal fibers measured with IHF and ordinate indicate that measured with IHI. They are expressed as a percentage value of the largest change in IHF (or IHI) with the minimal increase in interstimulus interval (0.1 ms) divided by the maximal IHF (or IHI). The solid lines indicate significant correlation between two different variables with P < 0.05. CS = conditioning stimulus, IHF = interhemispheric facilitation, IHI = interhemispheric inhibition, TS = test stimulus.