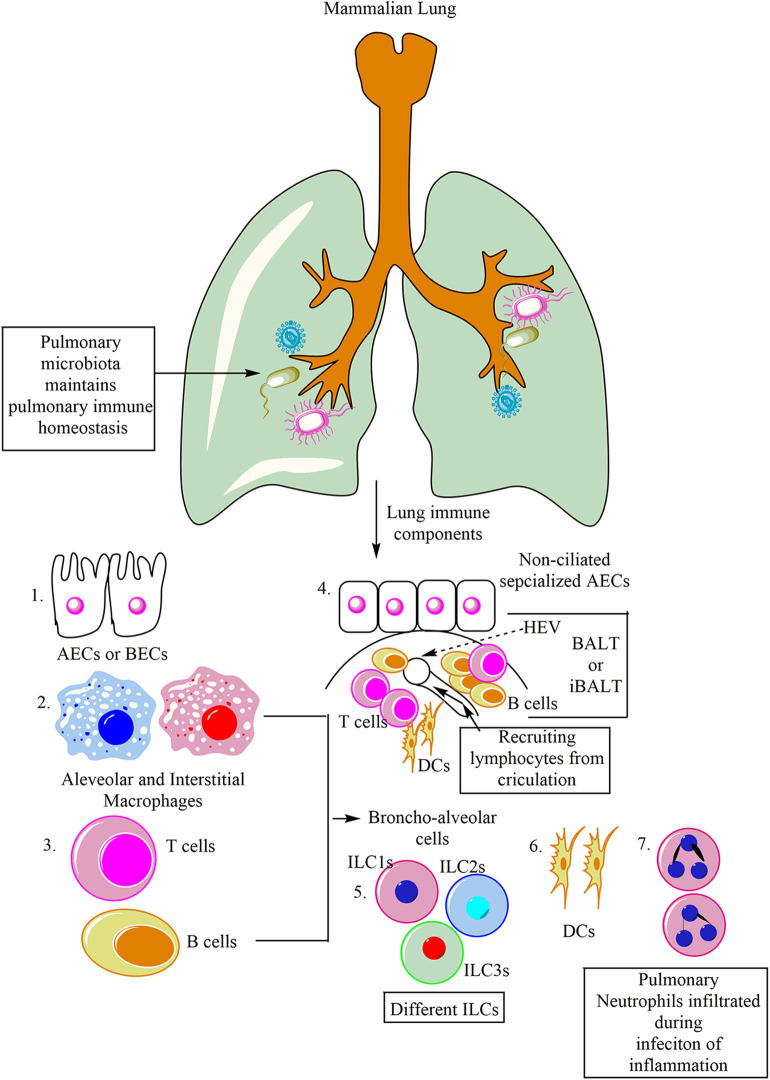
Figure 1.
Major immune cells in the mammalian lung. Lungs are potent immune organs and contain macrophages, which may be divided into alveolar macrophages (AM) and interstitial macrophages (IMs), alveolar and bronchial epithelial cells (AECs and BECs), DCs, NK cells along with other ILCs (ILC1s, ILC2s, and ILC3s), and adaptive immune cells (different T and B cells). Neutrophils also migrate to the lungs in response to the infection or inflammatory insult. Additionally, like Peyer's patches (PPs) of gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), lungs also have BALT. BALT contains T cells (T cell Zone), B cells (B cell zone), and DCs. The BALT induced in response to the infection is called iBALT.