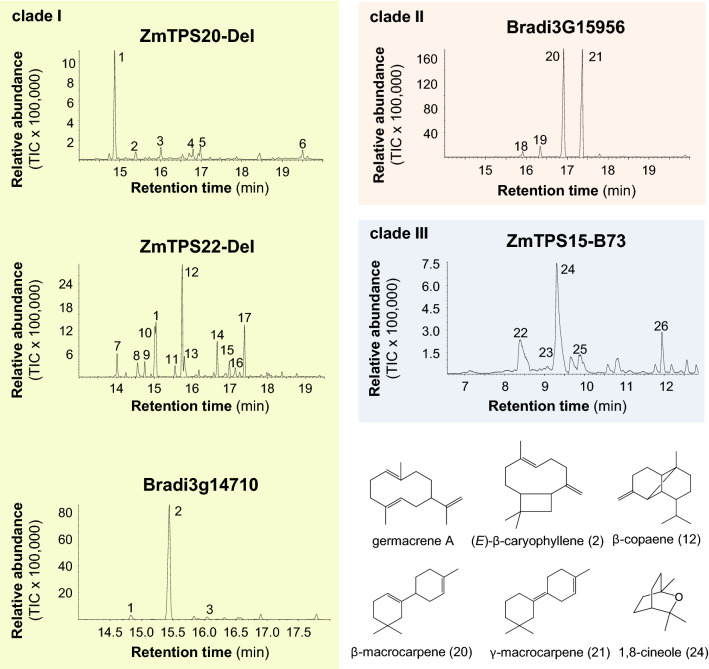
Fig. 3.
Characterization of selected terpene synthases from the Poaceae TPS-a clades I–III. Genes were heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli and partially purified proteins were incubated with (E,E)-FPP (TPS20-Del, TPS22-Del, Bradi3g14710, Bradi3g15956) or GPP (TPS15-B73). TPS reaction products were collected from the headspace of the enzyme assays using a solid phase microextraction (SPME) fiber and analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Total ion current chromatograms are shown. 1, β-elemene; 2, (E)-β-caryophyllene; 3, α-humulene; 4, unidentified sesquiterpene hydrocarbon1; 5, unidentified sesquiterpene hydrocarbon2; 6, unidentified sesquiterpene alcohol1; 7, δ-elemene; 8, unidentified sesquiterpene hydrocarbon3; 9, α-copaene; 10, β-cubebene; 11, β-ylangene; 12, β-copaene; 13, γ-elemene; 14, germacrene D; 15, α-muurolene; 16, cubebol; 17, δ-cadinene; 18, (E)-β-farnesene; 19, unidentified sesquiterpene hydrocarbon4; 20, β-macrocarpene; 21, γ-macrocarpene; 22, myrcene; 23, limonene; 24, 1,8-cineole; 25, (E)-β-ocimene; 26, linalool. Structures of major TPS products are shown