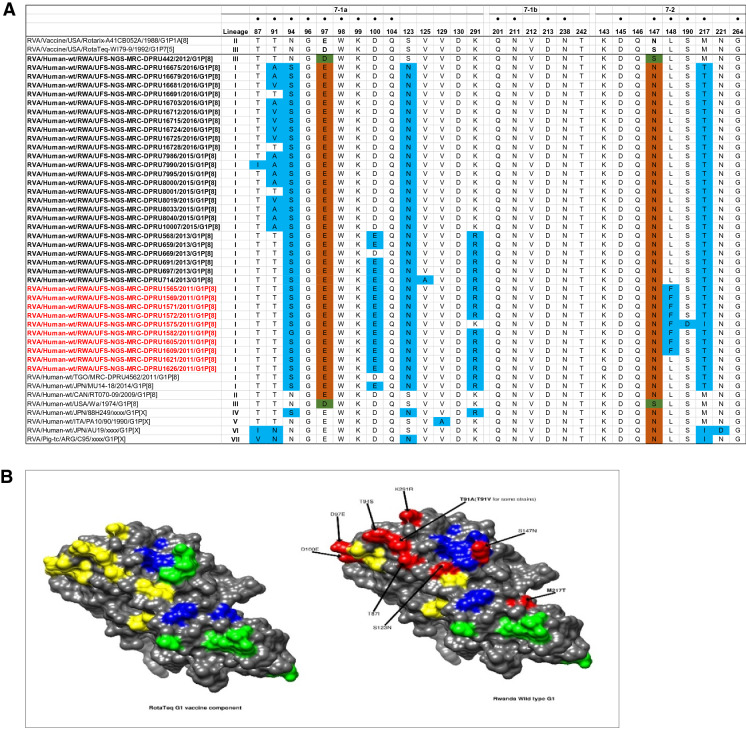
Figure 3.
(A) The alignment of the G1 component of Rotarix and RotaTeq vaccines and Rwandan wildtypes circulating from 2011- 2016 RVA seasons, based on the three VP7 antigenic residues (7-1a, 7-1b, and 7-2). Amino acids residues at positions 97 and 147 differ between Rotarix and RotaTeq and are indicated in boldface. Study strains amino acid residues highlighted in sky blue differs from both Rotarix and RotaTeq, while the green and brown colored residues are different from Rotarix and RotaTeq, respectively. The black dot indicates changes in the residues associated with escape neutralization with monoclonal antibodies. Post-vaccine and pre-vaccine G1P[8] study strains are bolded in black and red, respectively. (B) Location of surface-exposed amino acids differences between VP7 protein of RotaTeq G1 vaccine component versus a G1 wild-type strain from Rwanda (indicated in red). Antigenic epitopes in 3B are colored in yellow (7-1a), green (7-1b), and blue (7-2).