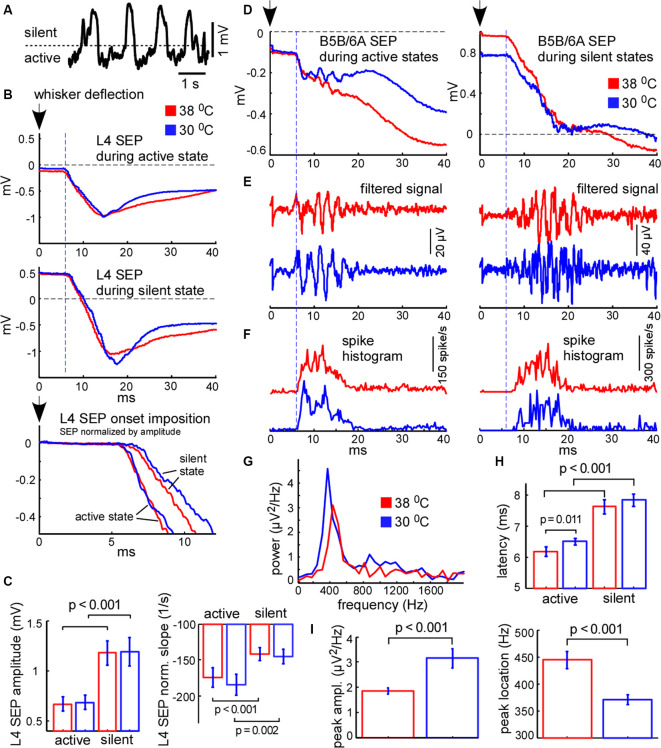
Figure 7.
Cortical sensory-evoked response in control and during cooling: active state vs. silent state. (A) Example of slow-wave activity in L5. The dashed line represents the threshold (0.4 standard deviations of the LFP signal), used for sensory stimuli sorting. (B) Examples of averaged L4 sensory-evoked potentials (SEPs) evoked during the active and silent states in control (shown with red) and cooling conditions (blue). The black arrow (zero time) represents the moment of principal whisker deflection. The lower trace represents a superposition of sensory evoked potential (SEPs) normalized by amplitude. (C) L4 SEP amplitude was significantly higher if evoked during the silent state compared to the active state independently of temperature (n = 22). The L4 SEP slope normalized by amplitude was significantly higher if evoked during active states. (D) Examples of averaged B5B/6A SEPs evoked during active states (left panel) and silent states (right panel) in control and cooling conditions. The original wide-band signal was averaged. Note high-frequency oscillation. (E) The same activities as in (D) band-passed within the 300–16,000 Hz range. Note sensory-evoked high-frequency oscillation. (F) Spike histograms (spikes collected from all recording channels) in control and during cooling. Note the higher latency of the sensory-evoked MUA response during the silent state compared to the active state. (G) The power spectrum plot calculated for the activities shown in (E) for active states. The power spectrum plot revealed a high-frequency oscillation peak. Note, that cortical cooling increased the peak amplitude and decreased the frequency of high-frequency oscillation. (H) The latencies of sensory-evoked MUA responses were significantly higher if evoked from silent states compared to active states. (I) Cortical cooling significantly increased the power of sensory-evoked high-frequency oscillation (peak amplitude) and decreased its frequency (peak location).