Figure 1.
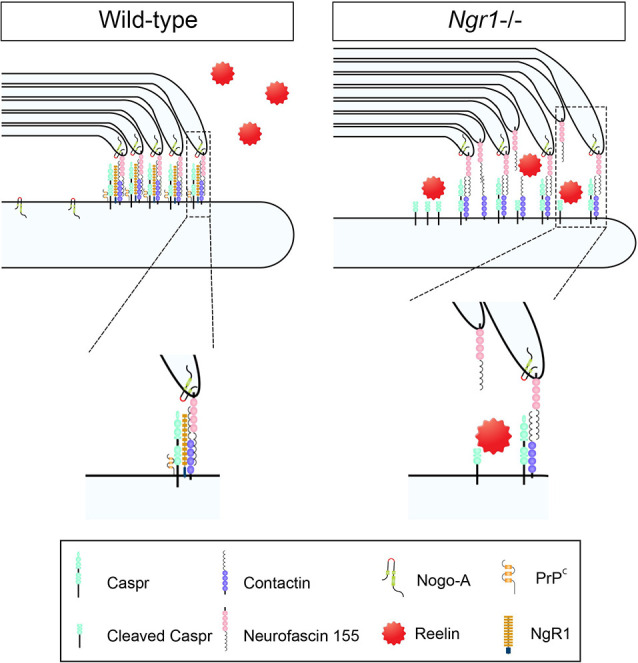
Axo-glial paranodal junctions and a potential regulatory role for Nogo receptor 1 (NgR1): evidence of a disrupted paranode in ngr1−/− mice. Schematic representation of the proposed unstructured paranodal septate junction in the central nervous system (CNS) myelinated fibers of ngr1−/− mice. The absence of NgR1 expression in neurons limits the capacity for cellular prion protein (PrPc) and contactin associated protein (Caspr) to interact, leaving Caspr as a substrate for intramembranous cleavage by Reelin. Expedited Caspr cleavage may promote the decompaction of myelin form the paranodal junctions altering the electrophysiological signature and potentially triggering the continuous turnover of myelin (adapted from Coman et al., 2006).
