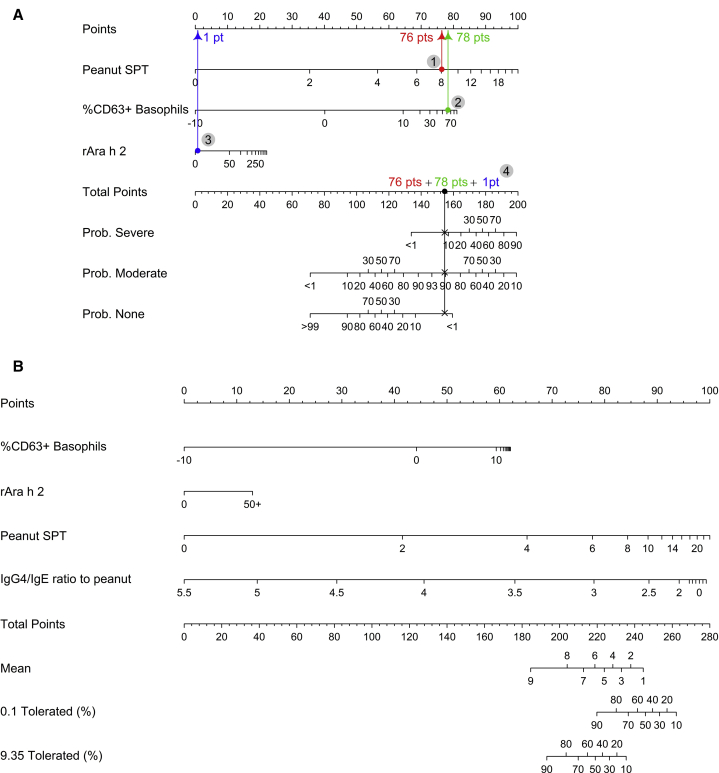
Fig 4.
Nomogram for predicting reaction severity using the BAT, the SPT, and level of Ara h 2–specific IgE (A) and nomogram for predicting cumulative dose threshold using the BAT, the SPT, level of Ara h 2–specific IgE, and IgG4/IgE ratio (B) on the basis of the LEAP and PAS studies when subjects were approximately 5 years of age. Predictions from the models can be made in a clinical setting by simply adding up points earned from each of the variable axes and then using that total to read estimated probabilities from the probability axes. A, For example, if we encounter a participant with an rArah h 2 level of of 1.5, a peanut SPT result of 8, and a BAT result of 53, we first find the value 1.5 along the axis associated with rArah h 2 (second from the top) and read vertically up to the corresponding point along the top Points axis (blue arrow). Similarly, we find the value 8 along the Peanut SPT axis and follow vertically to the Points axis to find that a Peanut SPT result of 8 earns about 76 points (red arrow). Similarly, a BAT value of 53 earns about 78 points (green arrow). Totaling the points earned from each variable gives 155 points for this participant. We find this total points value on the Total Points axis (fourth from the bottom) and imagine a vertical line extending down from that point intersecting each of the probability axes. These points of intersection are the predicted probabilities of falling into each of the severity categories. Given the values for the aforementioned hypothetical participant, we estimate less than a 10% chance of having a severe reaction, a 90% chance of having a moderate reaction, and less than a 10% chance of no reaction. B, For example, if we suppose that in addition to the biomarker values seen in (A), the participant has a log10-IgG4/IgE ratio to peanut of 1.6, the nomogram could be used if we wanted to estimate the mean cumulative tolerated dose, or the probabilities of having mean cumulative doses greater than 0.1 g or 9.35 g given these biomarker values. With a BAT value of 53 we accrue about 62 points, and with an Ara h 2 value of 1.5 we accrue about 5 points; a peanut wheal of 8 gives about 85 points, and an IgG4/IgE ratio of 1.6 gives about 95 points. This individual then has about 247 points in total, which gives an estimated mean cumulative tolerated dose of less than 1 g of peanut, a 45% chance of tolerating more than 0.1 g of peanut, and less than a 10% chance of tolerating more than 9.35 g of peanut. In fact, this individual had a severe reaction during the peanut double-blind placebo-controlled food challenge (DBPCFC) and tolerated 0 g of peanut.