Figure 2.
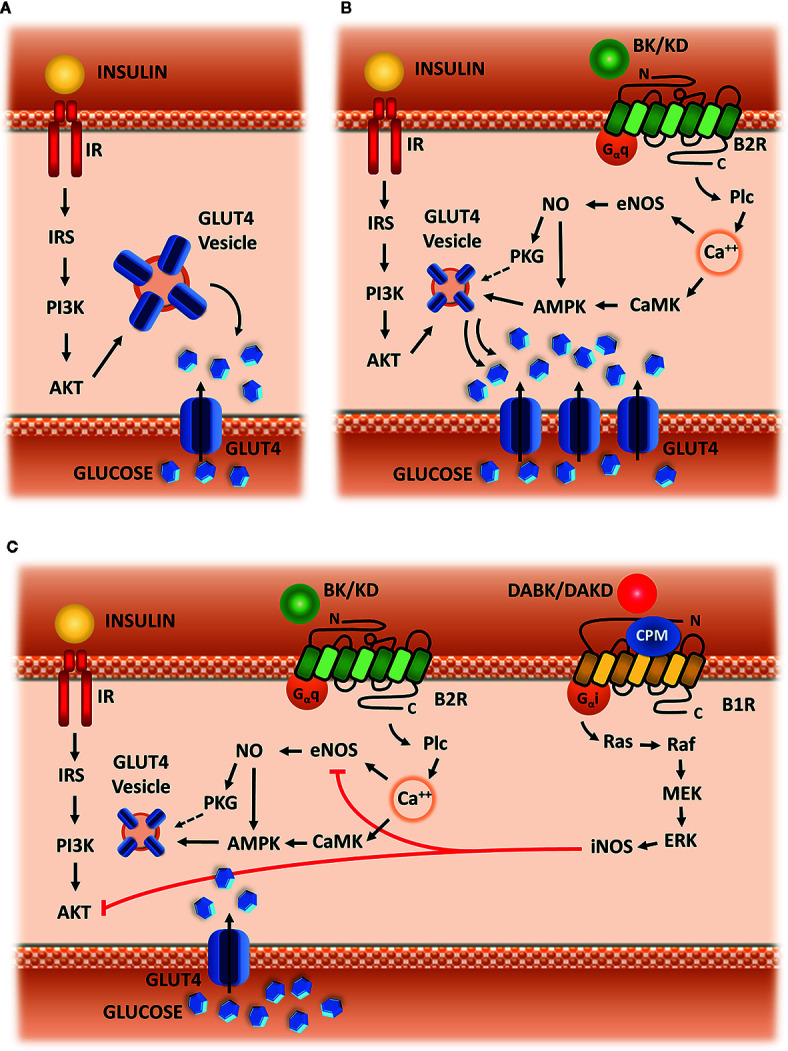
Hypothetic scheme. (A) Insulin signaling. Insulin-mediated glucose uptake in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle, which is triggered by IRS-1 phosphorylation, followed by activation of PI3k and AKT, leading to GLUT-4 translocation to membrane. (B) Kinin signaling via B2R. Signaling starts with Plc activation, followed by calcium release from intracellular storage, CAMK activation, eNOS phosphorylation and NO synthesis, leading to AMPK and PKG activation, and subsequently to increased GLUT4 translocation. (C) Kallikrein-Kinin System in glucose uptake. B1R is up-regulated in metabolic disturbances, as well as CPM enzyme, converting B2R agonists (BK or KD) into B1R agonists (DABK or DAKD). B1R pathway starts with the activation of G-alpha-i and beta-gamma subunit, leading to the activation of the following kinases: Src, Ras, Raf, MEK, and ERK.ERK activate iNOS leading to exacerbated NO production. Increased NO impairs glucose uptake, blocking eNOS and AKT activity.
