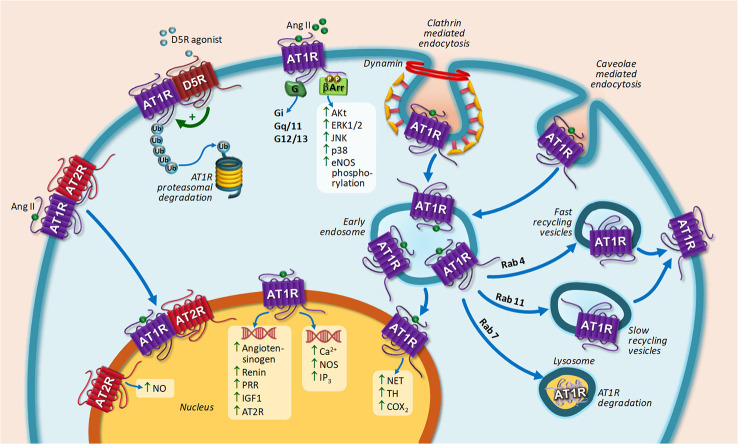
Figure 2.
Intracellular trafficking of AT1R and main biological responses coupled to nuclear AT1R or AT2R stimulation. AT1R stimulation by Ang II induces G-protein activation, including Gi, Gq/11, and G12/13 (canonical signaling pathway) and G-protein-independent signal transduction (non-canonical pathway) leading to ERK 1/2, JNK, Akt, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases activation, and eNOS phosphorylation through β-arrestin. Upon agonist stimulation, AT1R is internalized through CCPs and caveolae dependent pathways and then recycled back to the cell surface or targeted lysosome. AT1R-D5R heteromerization induced AT1R proteasomal degradation after D5R stimulation. AT1R translocation to the nucleus induces biological responses depicted in the scheme. AT2R translocation to the nucleus occurs by heteromerization with AT1R. Nuclear AT2R stimulation induced NO generation. Abbreviations: Ang II, Angiotensin II; AT1R, Ang II receptor type 1; AT2R, Ang II receptor type 2; D5R, dopamine receptor type 5; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; ERK1/2, Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; IP3, Inositol triphosphate; JNK, Jun N-terminal kinase; NET, norepinephrine transporter; NO, nitric oxide; PRR, pro-renin receptor; TH, tyrosine hydroxylase; β-arr, β-arrestin.