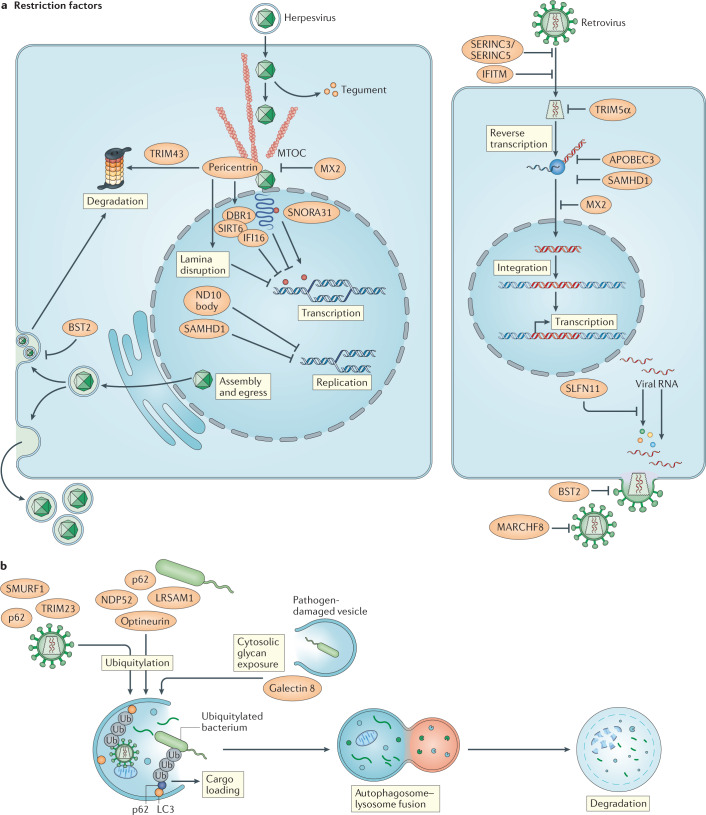
Fig. 4. Constitutive control of microbial replication by restriction factors and autophagy.
a | Restriction factors that control herpesvirus and retrovirus infections, including their targets in the viral replication cycle. Restriction factors interfere with viral replication by either blocking a specific and essential step in the viral replication cycle (for example, viral gene transcription or release of progeny virus) or depletion of factors that are essential for replication (such as deoxynucleoside triphosphates). b | Blockade of viral and bacterial replication by autophagy. Various ubiquitin E3 ligases (such as SMURF1, LRSAM1 and TRIM23) and ubiquitin-binding proteins (such as p62, optineurin and NDP52) have been identified to conjugate ubiquitin to microbial surfaces, which targets them for loading into autophagosomes. Also, cytosolic exposure of glycans by pathogen-damaged vesicles can be recognized by galectin 8 for targeting to autophagosomes. APOBEC3, apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing complex 3; BST2, bone marrow stromal antigen 2 (also known as tetherin); DBR1, RNA lariat debranching enzyme 1; IFI16, interferon-γ-inducible protein 16; IFITM, interferon-induced transmembrane protein; MTOC, microtubule-organizing centre; ND10, nuclear domain 10; SAMHD1, SAM domain and HD domain-containing protein 1; SIRT6, sirtuin 6; SNORA31, small nucleolar RNA, H/ACA box 31.