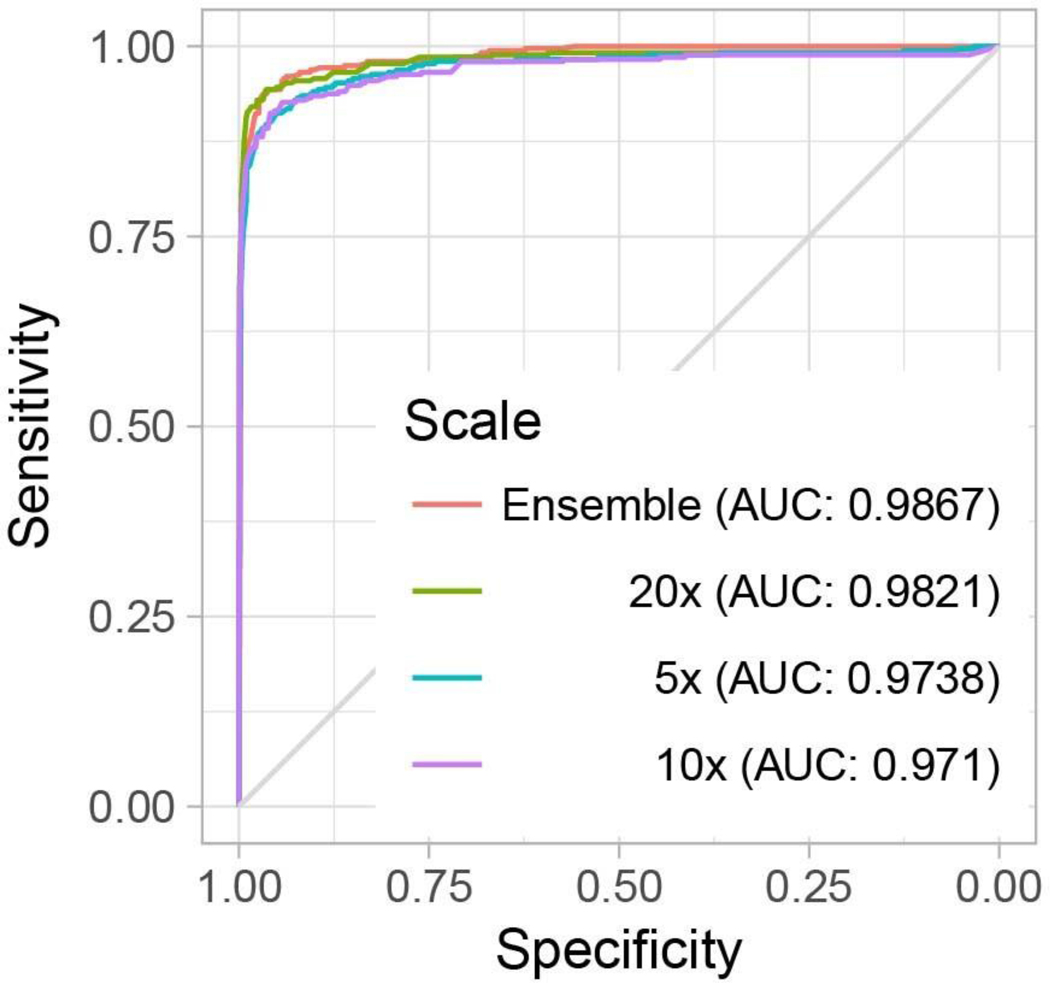
Extended Data Fig. 4 |. Performance of the MiL-RF model at multiple scales on the prostate dataset.
The MIL model was run on each slide of the test dataset (n = 1,784) with a stride of 40 pixels. From the resulting tumor probability heat map, hand-engineered features were extracted for classification with the random forest (RF) model. The best MIL-RF model (ensemble model; AUC = 0.987) was not statistically significantly better than the MIL-only model (20× model; AUC = 0.986; see Fig. 3), as determined using DeLong’s test for two correlated ROC curves.