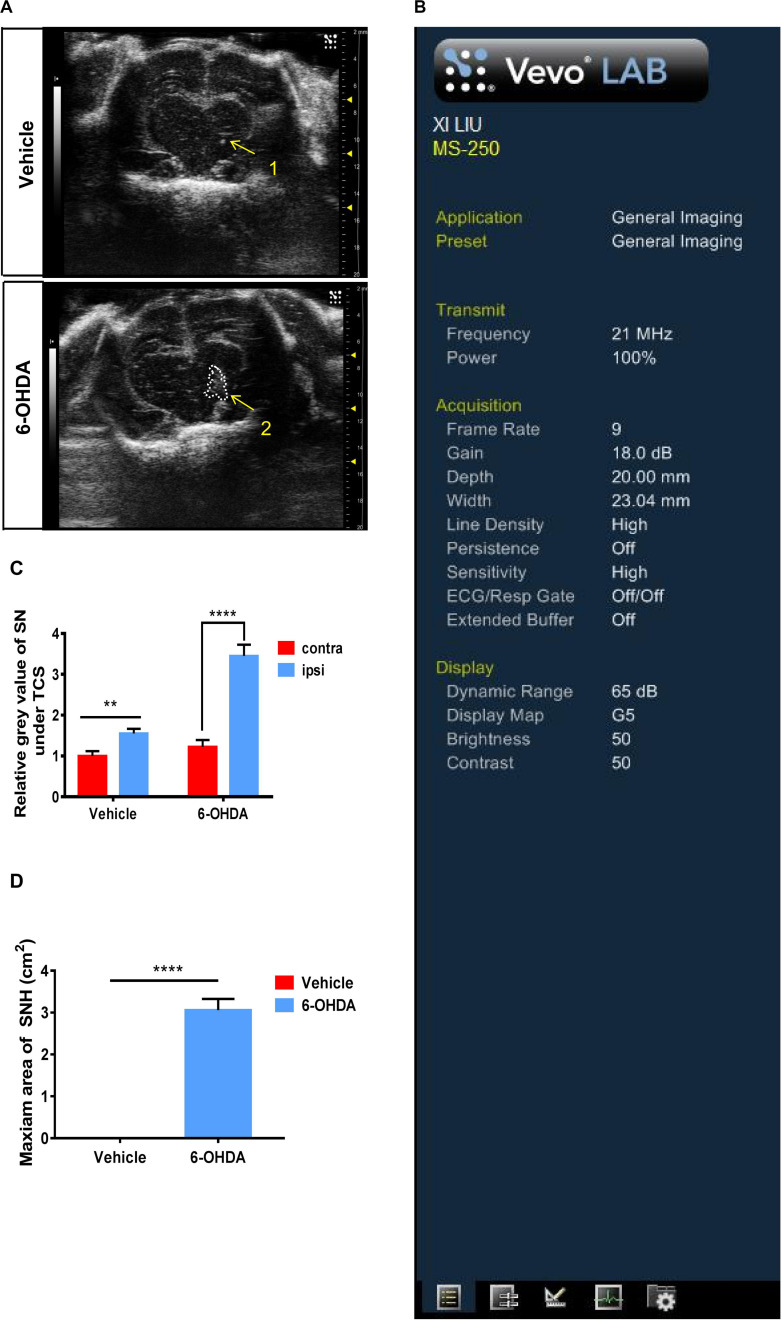
FIGURE 1.
Transcranial sonography (TCS) images and qualification of substantia nigra hyperechogenicity (SNH) after unilateral stereotactic surgery. Male rats were injected with either 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) (n = 10) or vehicle (n = 10). At 15 days after surgery, TCS detection was performed. (A) Image of the midbrain plane showing a significant hyperechogenicity of 6-OHDA-lesioned rats (2), while only a scatter echo corresponding to the shape of the needle was observed in the vehicle group (1). Area 2 = 3.057 cm2. (B) General condition of TCS detection. (C) Statistical result of the mean gray values of substantia nigra (t-test). Vehicle group: P = 0.0015, t = 3.35, df = 50, F = 1.002. 6-OHDA group: P < 0.0001, t = 6.935, df = 52, F = 2.713. (D) Statistical result of the maximum SNH area (t-test). P < 0.0001, t = 11.44, df = 12. *Comparison between contralateral and ipsilateral from a single group. ns P > 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.