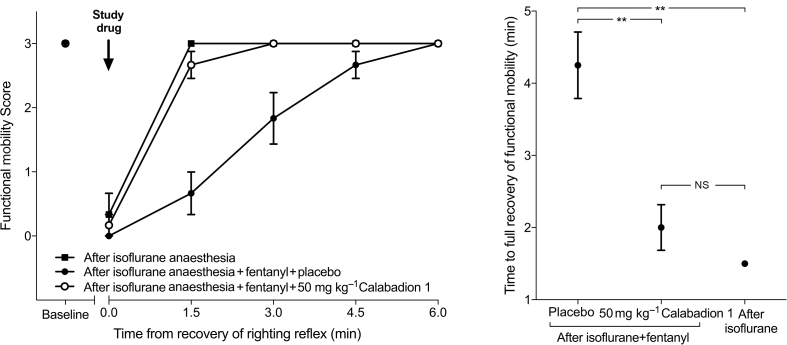
Fig 4.
Acceleration of postanaesthesia recovery of functional mobility by Calabadion 1. Time to recovery of full functional mobility was assessed by the balance beam test. After recovery of righting reflex, the time rats remained on the balance beam was measured to evaluate balance and body strength on a scale of 0 (inability to maintain grip or balance) to 3 (ability to reach support at the other end of the beam). Animals were randomised to receive either i.v. Calabadion 1 (50 mg kg−1; n=6) or placebo (n=6). Additionally, functional mobility was assessed after isoflurane-only anaesthesia (n=6). Time to full recovery of functional mobility after isoflurane/fentanyl anaesthesia was less after administration of Calabadion 1 (50 mg kg−1) compared with placebo (∗∗P<0.01). The effect of Calabadion 1 was comparable with recovery times after fentanyl-free isoflurane-only anaesthesia. Data are reported as mean (standard error of the mean). NS, not significant.