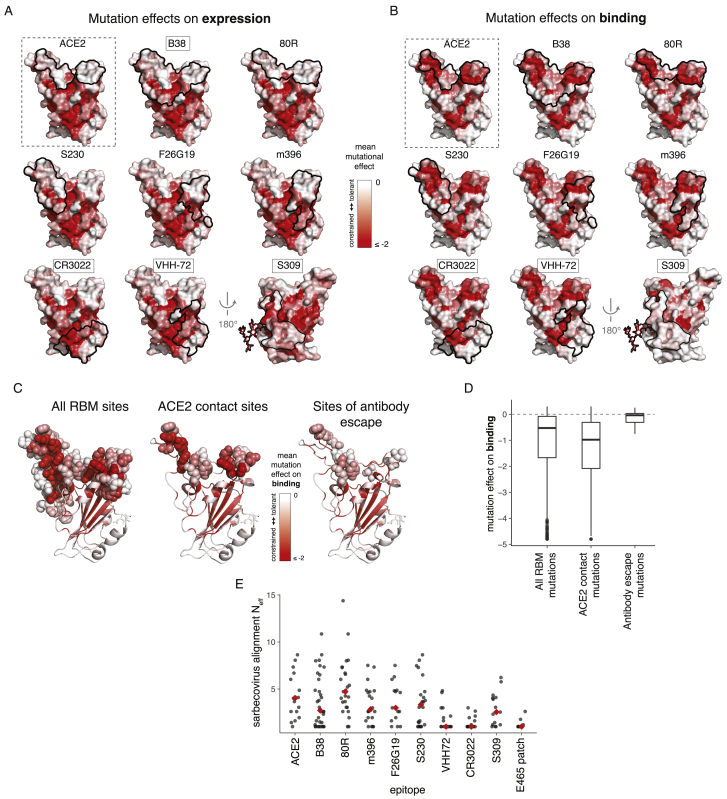
Figure S6.
Mutational and Evolutionary Constraint of Antibody Epitopes, Related to Figure 6
(A, B) Surface representations of antibody epitopes colored by mutational effects on expression (A) and binding (B). Representations as described in Figure 6A. (C, D) Mutational constraint and observed antibody escape mutations. Baum et al. (Baum et al., 2020) selected SARS-CoV-2 escape mutations from RBD-directed antibodies. We compare the average mutational tolerance of the sites at which these escape mutations accrue (C), and the effects of the specific escape mutations themselves (D) to all RBM and ACE2-contact sites/mutations. The antibody escape involved mutations that were better tolerated than typical mutations in the RBM or ACE2-binding interface. (E) Evolutionary diversity in antibody epitopes and our newly described E465-centered surface patch among the sarbecoviruses in Figure 1A. Diversity is summarized as the effective number of amino acids (Neff), which scales from 1 for a site that is invariant, to 20 for a site in which all amino acids are at equal frequency.